Engine cooling system:
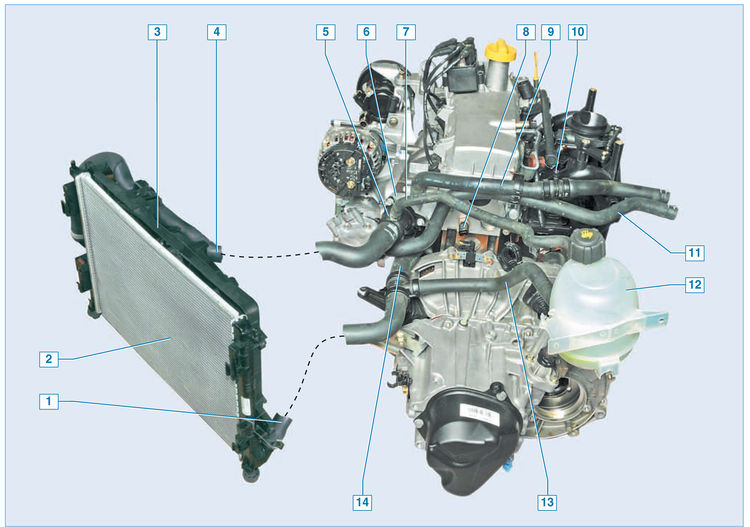
1 - outlet hose of the radiator;
2 - radiator;
3 - fan casing;
4 – a bringing hose of a radiator;
5 - thermostat housing;
6 – a final branch pipe of a head of the block of cylinders;
7 - steam outlet hose;
8 - coolant temperature sensor;
9 - inlet hose of the heater radiator;
10 - air outlet fitting;
11 - outlet hose of the heater radiator;
12 - expansion tank;
13 - inlet hose;
14 - inlet pipe of the coolant pump
Cooling system - liquid, closed type, with forced circulation. It consists of an expansion tank, a coolant pump, an engine cooling jacket, a thermostat, connecting hoses and a radiator with an electric fan. The heater core is connected to the cooling system. The system is filled with coolant through the neck of the expansion tank.
Expansion tank elements:

1 - tank;
2 – a cover of a jellied mouth;
3 - steam outlet hose;
4 - inlet hose
The expansion tank is made of translucent plastic, which allows you to visually control the level of the coolant. On the wall of the expansion tank there are marks MAX and MIN, between which there should be a liquid level on a cold engine. A steam outlet hose is connected to the upper fitting of the tank, connecting the tank to the thermostat housing.
The lower fitting of the tank is connected by an inlet hose to the outlet (lower) hose of the radiator and the inlet pipe of the pump.
Expansion tank cap

The tightness of the cooling system is ensured by inlet and outlet valves in the cap of the expansion tank.
The exhaust valve maintains a higher than atmospheric pressure in the system on a hot engine. This increases the boiling point of the coolant and reduces steam losses. The intake valve opens when the pressure in the system drops when the engine is cold. At the same time, the coolant level in the expansion tank is reduced. If the expansion tank cap is lost, it must not be replaced with a sealed cap without valves.
The union for release of air from the cooling system

The hose for supplying fluid to the heater has a fitting for venting air from the cooling system when it is filled with fluid.
The fitting is closed with a cap. \
Coolant pump:

1 - body;
2 - impeller
The circulation of liquid in the cooling system is provided by the coolant pump. The coolant pump is a vane, centrifugal type, driven by a timing belt from the crankshaft toothed pulley. It consists of a housing, a bearing assembly with a seal, an impeller and a toothed pulley.
The liquid enters the pump through a supply pipe located on the front wall of the cylinder block under the exhaust manifold.
From the pump, liquid under pressure is supplied to the engine cooling jacket, and from there to the outlet pipe of the cylinder head, to which the thermostat housing is attached.
Thermostat

On a cold engine, the thermostat valve is closed and closes the thermostat housing pipe leading to the radiator of the cooling system. In this case, all the liquid through the outlet pipe of the cylinder head enters the heater radiator, bypassing the cooling system radiator, and returns to the pump - a small circulation circle.
As the engine warms up, at a fluid temperature of 89 ° C, the thermostat valve begins to move, allowing fluid to flow into the radiator of the cooling system.
At a temperature of 95 ± 2 ° C, the thermostat valve opens completely and the liquid enters the radiator of the cooling system, where it gives off heat to the surrounding air.
The movement of fluid through the engine cooling jacket and the cooling system radiator forms a large circulation circle. The liquid circulates through the heater radiator constantly and regardless of the position of the thermostat valve.
Radiator:

1 - rubber cushion of the lower mount;
2 - outlet pipe;
3 - left tank;
4 – top fastening pin;
5 - inlet pipe;
6 - right tank
The radiator of the cooling system consists of two vertically located plastic tanks connected by aluminum tubes with cooling plates. The liquid enters the radiator through the upper pipe, and is discharged through the lower one. The radiator does not have a drain hole.
Cooling fan assembly with radiator:

1 - additional resistor;
2 - casing;
3 - electric motor;
4 - impeller
The electric fan is installed in the casing behind the radiator. The blades of the fan impeller are located on the hub with variable pitch.
With an increase in the temperature of the coolant, the fan turns on at the command of the electronic control unit (ECU) of the engine through a relay.
Additional fan resistor

On vehicles equipped with air conditioning, an additional resistor is installed on the fan shroud. When the coolant temperature rises or when the air conditioner is turned on, the computer turns on the fan through an additional resistor and the fan rotates at low speed. With a further increase in the temperature of the liquid and reaching the value of the refrigerant pressure above the threshold level, the ECU turns on the electric motor, bypassing the resistor, and the fan rotates at high speed.
coolant temperature sensor

The coolant temperature sensor is installed at the end of the cylinder head on the left side in the direction of the vehicle.
The sensor provides information to the temperature gauge in the instrument cluster and the engine control electronics.
Source: http://wiki.zr.ru/124-2_%D0%A0%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%82_Stepway









![1 generation [2009 - 2014]](/uploads/Renault_Sandero_2009-2014_.jpg)
