 Picture 1
Picture 1
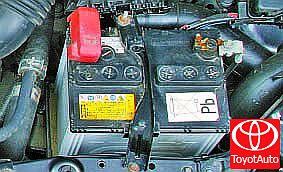
The manufacturer installs a battery with a nominal voltage of 12 V and a capacity of 60 Ah on Toyota Corolla cars. The battery elements are located in a polypropylene monoblock and are closed by a common cover, inseparably connected to the monoblock. The battery cover has plugs for topping up with distilled water.
A modern car is saturated with various consumers of electricity, electronic devices, from the audio system to the blocks of electronic engine control systems, gearboxes, anti-lock brakes, airbags, etc. In the wet off-season, and especially in winter, all automotive electrics and electronics, and especially the car battery, are tested for endurance.
As practice shows, if there are problems with starting the engine in the cold season and to solve them, you constantly have to recharge the battery, provided that the generator is in good condition and the tension of the auxiliary drive belt is normal, and the battery life exceeds 3 years, it is quite reasonable to get up question about buying a new battery.
Modern batteries are usually of two types:
- maintenance-free during the entire service life;
- low-maintenance, requiring topping up with distilled water once or twice a year.
It is advisable to choose for your car, taking into account the recommendations of the manufacturer, a maintenance-free battery from a wide range of car batteries from various manufacturers on the automotive aftermarket.
It must be remembered that at low temperatures, due to an increase in the viscosity of engine oil and a deterioration in the ignition conditions of the fuel, the power consumed by the starter when starting the engine increases by two to three times. The starting time of a cold engine in comparison with a warm one in some cases increases by 10-20 times. Thus, in winter, at low air temperatures, increased requirements are placed on the starter characteristics of the battery, i.e. to its ability for a short time (10 s according to GOST) to deliver the required current necessary for the operation of the starter with the nominal speed of its armature in the cold season (-18 ° C according to GOST).
The manufacturer installs a lead-acid battery with a nominal voltage of 12 V and a capacity of 60 Ah on the car.
 Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Battery device:
1 - common cover;
2 - terminal "plus";
3 - density indicator float;
4 - partitions of elements;
5 - monoblock (body);
6 - electrolyte density indicator;
7 - terminal "minus";
8 - battery cell.
Possible battery malfunctions, their causes and solutions
NOTE
The principle of operation of lead-acid batteries is based on the electrochemical reactions of lead and lead dioxide in a sulfuric acid environment. During the discharge, lead dioxide is reduced at the cathode and lead is oxidized at the anode. When charging, reverse reactions occur, to which, at the end of the charge, the water electrolysis reaction is added, accompanied by the release of oxygen at the positive electrode and hydrogen at the negative.
A lead-acid battery cell consists of positive and negative electrodes, separators (separating grids) and an electrolyte. The positive electrodes are a lead grid in which the active substance is lead peroxide (PbO2). The negative electrodes are also a lead grid with spongy lead as the active substance. In practice, 1–2% antimony is added to lead gratings to increase mechanical strength. Currently, calcium salts are used as an alloying component in both plates or only in positive ones (hybrid technology). The electrodes are immersed in an electrolyte consisting of an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The highest conductivity of this solution at room temperature (which means the lowest internal resistance and the lowest internal losses) is achieved at its density of 1.26 g/cm3. However, in practice, in regions with a cold climate, higher concentrations of sulfuric acid are also used - up to 1.29-1.31 g/cm3. This is because when a lead-acid battery is discharged, the density of the electrolyte drops and its freezing point becomes higher, a discharged battery may not withstand the cold.
In new designs of rechargeable batteries, lead plates (grids) are replaced with foamed carbon covered with a thin lead film, and the liquid electrolyte is gelled with silica gel to a pasty state. Using less lead and distributing it over a large area, the battery is made not only more compact and lighter, but also much more efficient: in addition to greater efficiency, it charges much faster than previous generation batteries.
The battery elements are located in a polypropylene monoblock (case) 5 (Figure 2) and are closed by a common cover 1, inseparably connected to the monoblock. The two vents on the sides of the battery at the top allow the small amount of gas generated in the battery to escape.
An electrolyte density indicator 6 can be mounted in the battery cover, the readings of which take into account the temperature of the battery. There are three options for the indicator readings:
- green dot - battery is charged;
- a dark indicator without a green dot - the battery is partially discharged, starting the engine is difficult or impossible;
- a transparent or light yellow indicator - an excessive decrease in the electrolyte level due to a long recharge of the battery or its natural wear.
NOTE
Instead of a regular maintenance-free battery, you can install any battery of other manufacturers that is similar in capacity and mounting dimensions. In this case, use and maintain the battery in accordance with the instructions supplied with it.
Source: http://toyotauto.net/corolla/osobennosti-konstrukcii-akkumulyatornoy-batarei.html






![E140/E150 [2006 - 2010]](/uploads/Toyota_Corolla_E140_2006_-_2010_.jpg)
