General information
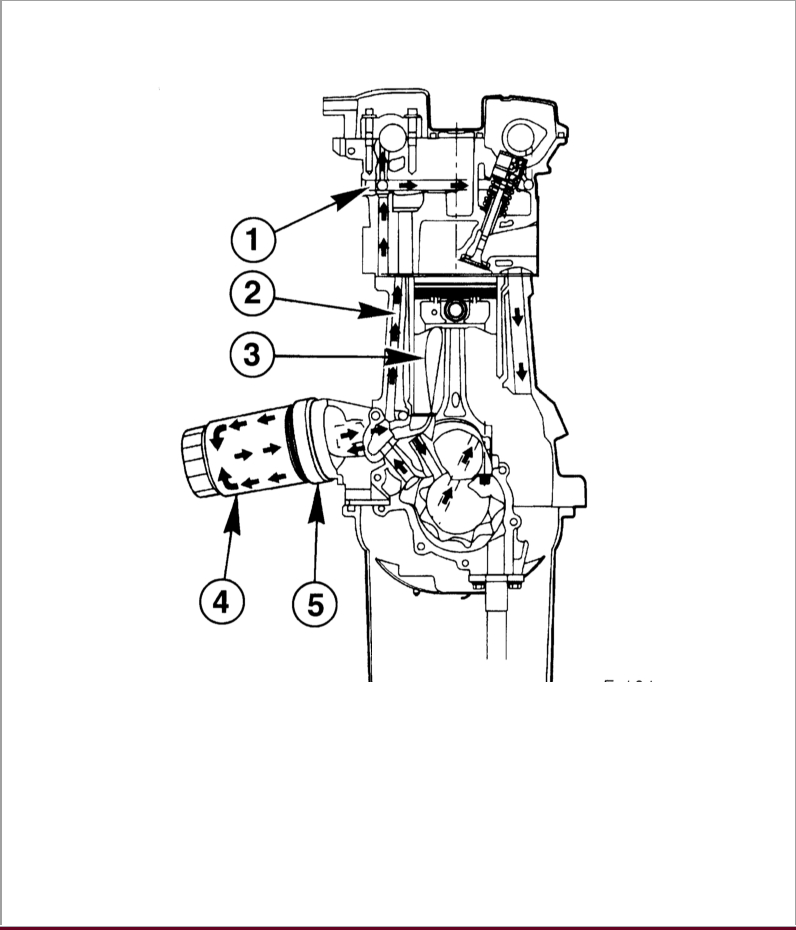
Engine lubrication system:
1 - oil channel of the cylinder head;
2 - main oil line;
3 - oil injection for piston cooling;
4 - oil filter of the main flow;
5 - oil cooler.
Notes:
The illustration is informative and may not fully correspond to the model in question.
4-cylinder petrol engine 111
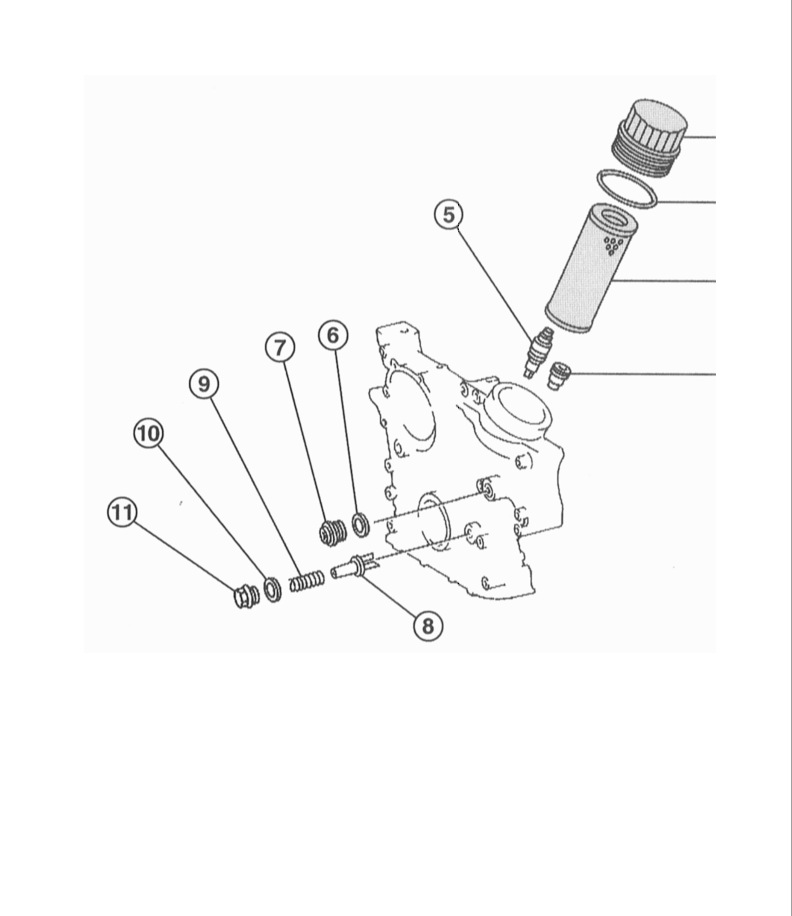
Oil filter:
1 - oil filter cover;
2 - sealing ring;
3 - filter element;
4 - bypass valve;
5 - idle valve;
6 - sealing ring;
7 - threaded plug;
8 - check valve;
9 - spring;
10 - sealing ring;
11 - cork.
6-cylinder petrol engine 112
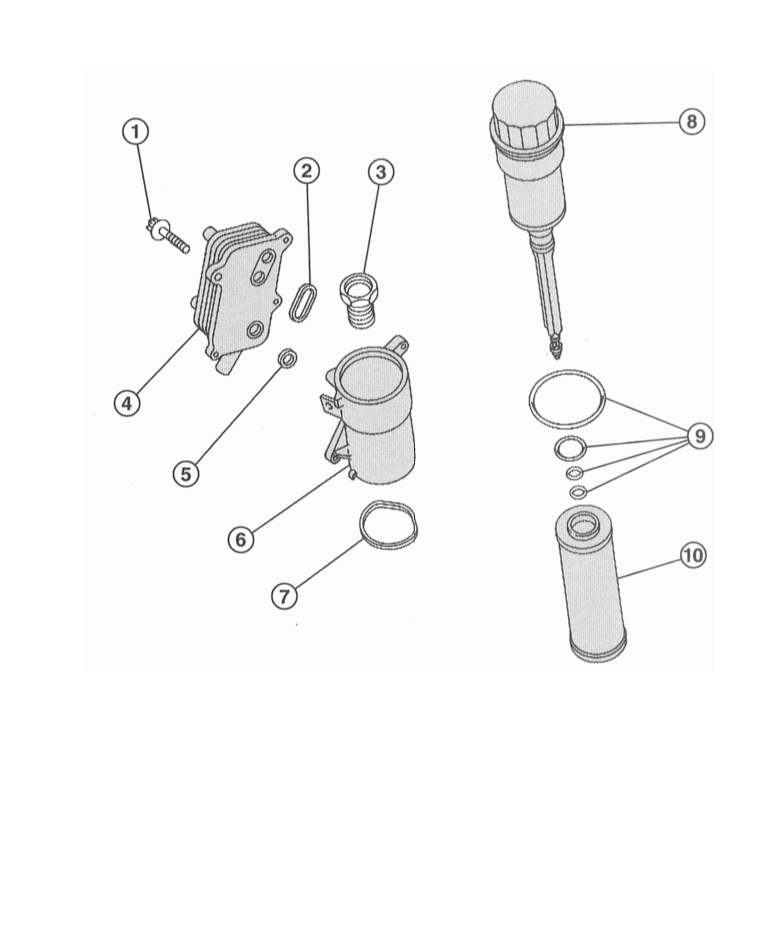
Oil filter:
1 - bolt, 11Nm;
2 - sealing ring;
3 - fitting;
4 - oil cooler;
5 - sealing ring;
6 - filter housing;
7 - sealing ring;
8 - oil filter cover;
9 - set of sealing rings;
10 - filter element.
Diesel engines
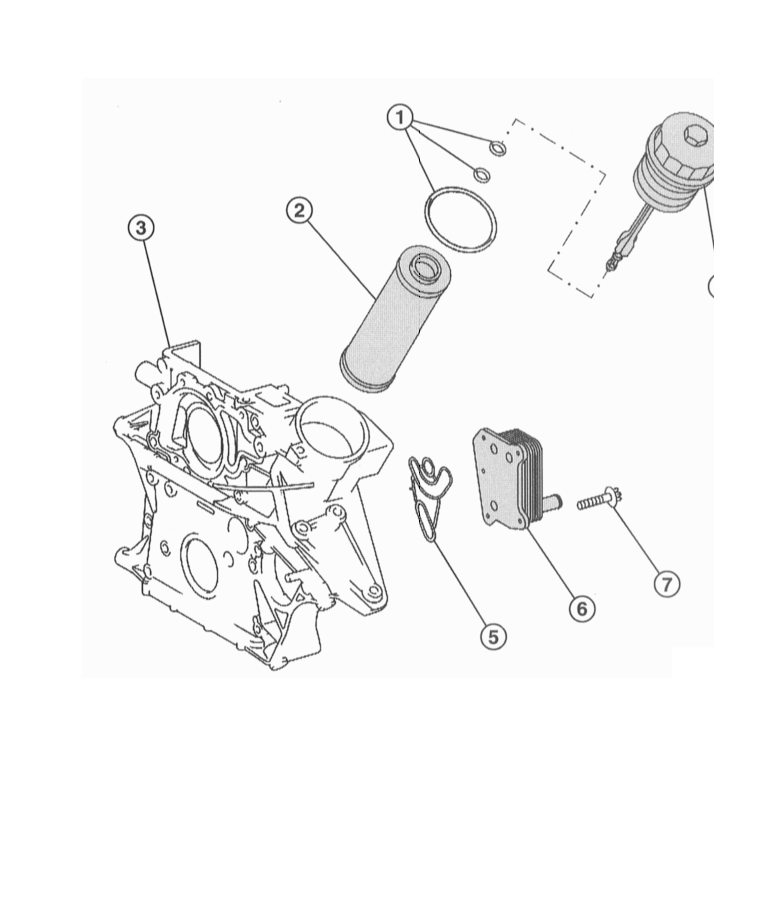
Oil filter:
1 - set of sealing rings;
2 - filter element;
3 - casing of the distribution mechanism;
4 - oil filter cover;
5 - sealing gasket of the oil cooler;
6 - oil cooler;
7 - bolt.
The engines are equipped with a circulating pressure lubrication system. The oil pump draws oil through a screen from the oil pan and pressurizes it into the system through the oil filter. There is a pressure reducing valve at the outlet of the oil pump. When the pressure rises above the set value, the valve opens and part of the oil drains back into the oil pan.
Through the central hole of the oil filter, oil enters directly into the main channel. When the oil filter is clogged, the bypass valve sends oil into the system unfiltered.
Channels for lubricating the crankshaft bearings branch off from the main oil line. Through inclined holes in the crankshaft, oil is supplied to the connecting rod bearings. To cool the pistons, oil is injected onto them from below through nozzles.
At the same time, oil reaches the cylinder heads through vertical galleries and enters to lubricate the camshaft bearings and elements of the valve mechanisms of the gas distribution system.
Depending on the engine power, the oil can be cooled in an additional oil cooler located on the side of the oil filter housing and included in the engine cooling circuit.
Oil consumption
For internal combustion engines, oil consumption refers to the amount of oil that is consumed as a result of the combustion process. Oil consumption should not be confused with oil loss due to leaks in the oil pan, cylinder head cover, etc.
Normal oil consumption occurs due to the combustion of a small amount of oil in the cylinders, due to removal with combustion products and wear products. In addition, oil is lost due to the high combustion temperatures and high pressures that occur during engine operation. Oil consumption is also affected by external operating conditions, such as driving style, as well as manufacturing tolerances of engine parts. Oil consumption should not exceed 0.8 l/1000 km.
Notes:
Never fill oil above the Max. If an excess amount of oil has been poured, it must be removed. Otherwise, the catalytic converter may be damaged, as unburned oil enters the exhaust system.
Source: http://carpedia.club/
![W203/S203/CL203 [2000 - 2004]](/uploads/mercedes-c-klass-w203.jpg)
