The fuel vapor recovery system prevents the release of fuel vapors from the power supply system into the atmosphere, which adversely affect the environment.
The system uses the method of vapor absorption by a carbon adsorber. It is installed under the right front fender (the fender liner is removed for clarity) and is connected by steam lines to the fuel tank and intake pipe.

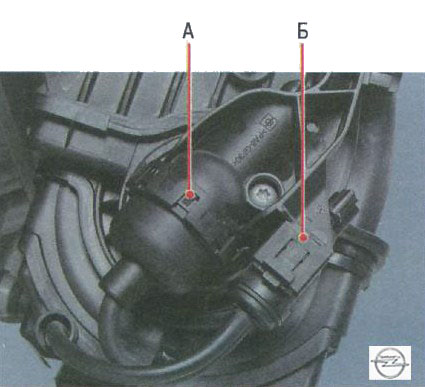
On the bracket mounted on the Astra intake pipe, there is an adsorber purge solenoid valve, which switches the system operating modes based on signals from the engine control unit.

Fuel vapors from the fuel tank are constantly discharged through the steam pipeline and accumulate in the adsorber filled with activated carbon (adsorbent). When the engine is running, the adsorbent is regenerated (recovered) by blowing the adsorber with fresh air entering the system under the action of vacuum transmitted through the steam line from the inlet pipe to the adsorber cavity when the valve is opened. The value of the valve opening, and, consequently, the intensity of the purge of the adsorber depends on the angle of rotation of the throttle valve and is determined by the vacuum that occurs in the cavity of the intake pipe of a running engine.
Fuel vapors from the adsorber through the steam line enter the engine intake pipe and burn in the cylinders.
Malfunctions of the fuel vapor recovery system entail idle instability, engine stop, increased toxicity of exhaust gases and deterioration in driving performance of the Opel Astra.
- Source http://www.automnl.com/model/opel_astra_h2/301/





![G [1998 - 2009]](/uploads/Opel_Astra_II_G_1998_-_2009_.jpg)
![H [2004 - 2011]](/uploads/remont-opel-astra-family.jpg)
