Instruments:
- Nozzle on the crank 10 mm
- Collar for end nozzle
- plumb line
- Telescopic ruler
Parts and consumables:
- Chalk
Notes:
Checking and adjusting wheel alignment is necessary to ensure good vehicle stability and handling, as well as uniform tire wear during operation.
Check and adjust the angles of the wheels on special stands according to the instructions for their operation. The discrepancy between the actual values measured on the vehicle and the control values is due to wear and deformation of the suspension parts or deformation of the body.
Warning:
Replacing or repairing suspension parts can change wheel alignment, so checking wheel alignment is a must.
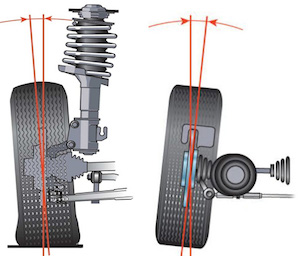
– When checking and adjusting the front wheel alignment, first check the caster angle, then the camber angle, and lastly the toe-in.
– The angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the front wheel is formed by a vertical and a line passing through the middle of the upper support of the telescopic strut and the center of the sphere of the ball bearing, fixed on the lower arm of the front suspension. Adjusting the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation is not provided for by the design of the car. If the angle deviates from the nominal value, replace damaged and deformed parts.
– The camber angle of the front wheels is characterized by the deviation of the mean plane of rotation of the wheel from the vertical. Adjustment of a corner of disorder of forward wheels is not provided by a design of the car.
– The toe-in of the front wheels is the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. The convergence of the front wheels is regulated by changing the length of the steering rods. Check the following rear wheel alignment.
– The camber angle of the rear wheels is characterized by the deviation of the mean plane of rotation of the rear wheel from the vertical. Adjusting the angle of the rear wheels camber is not provided for by the design of the car. The convergence of the rear wheels is the angle between the plane of rotation of the rear wheel and the longitudinal axis of the car.
Front wheel camber adjustment:
1. First, the self-locking nuts on the bolts are loosened (about one turn), and then the camber angle is adjusted with the lower adjusting bolt, installed with the hex head back along the vehicle.

Note:
When turning this bolt clockwise one turn, the camber angle increases by approximately 0°5', when rotated in the opposite direction, it decreases.
Rear wheel camber adjustment:
1. The camber angle of the rear wheels is adjusted by turning the adjusting bolts securing the front lower arm to the rear suspension cross member.

Note:
Clockwise rotation of the adjusting bolt for the left wheel increases the camber, for the right it decreases.
Vehicle wheel alignment angles:
After the first maintenance (after 2000–3000 km of run) and during the further operation of the car, the value of the wheel alignment angles should be:
- Longitudinal angle of inclination of the axis of rotation - 4°±30' (3°30'±30');
- Camber - 0°30'±20' (0°5'±20');
- Convergence - 2/4 mm (3/5 mm).
Note:
The difference in the longitudinal angles of inclination of the axes of rotation of the right and left wheels should not exceed 0°30'.
The article is missing:
- High-quality repair photos
- Tool photo
Source: http://nissan-qashqai.dv13.ru/proverka-i-regulirovka-uglov-ustanovki-koles/









![1 generation [2007 - 2010]](/uploads/Nissan_Qashqai_2007-2010_.jpg)
