The engine management system consists of an electronic control unit (ECU), sensors for engine and vehicle operation parameters, as well as actuators.
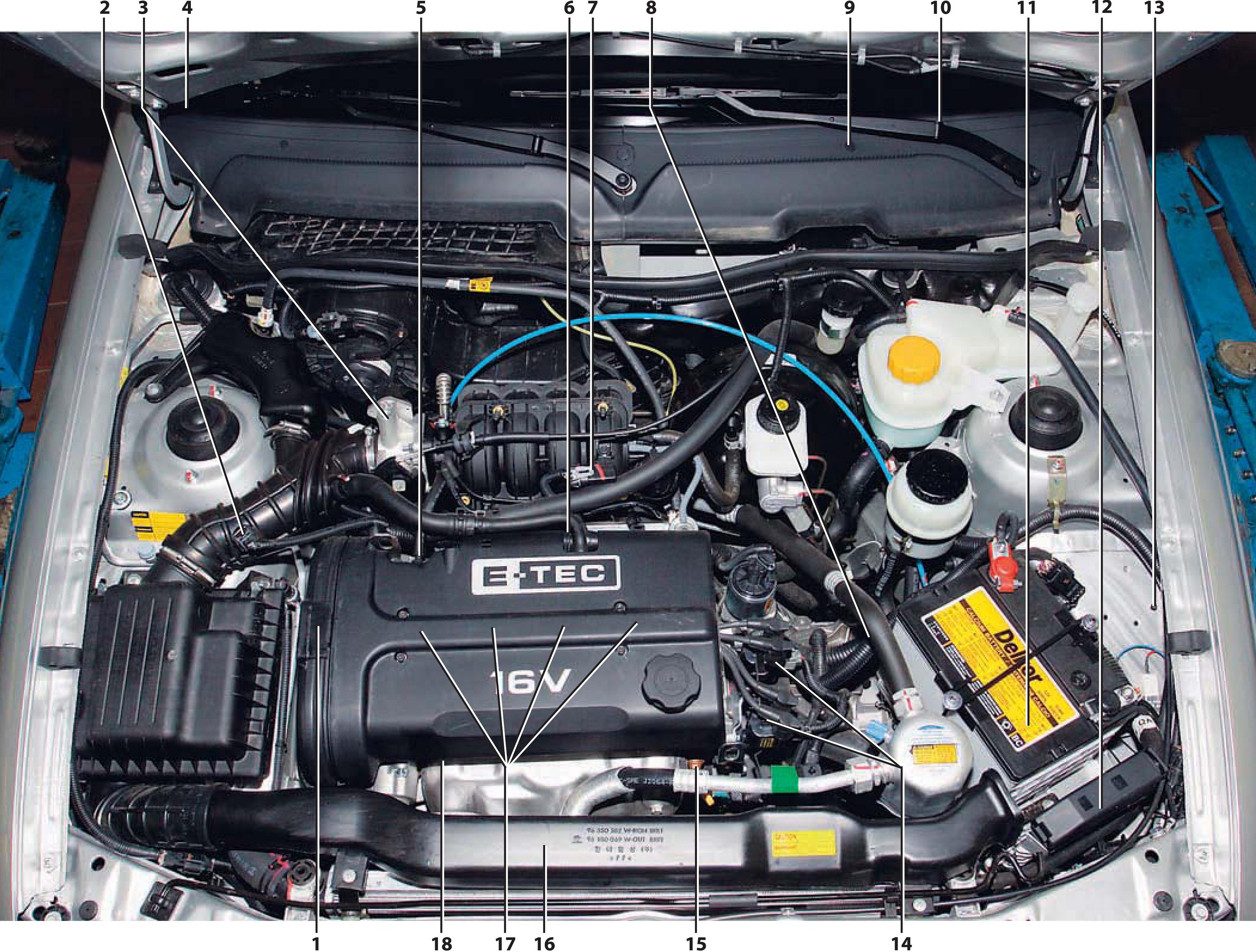
Elements of the electronic engine management system F16D3 :
1* – phase sensor;
2 - air temperature sensor at the inlet to the engine;
3* - throttle position sensor;
4* - diagnostic block;
5* - coolant temperature sensor;
6* - knock sensor;
7 – the sensor of absolute pressure of air on an inlet;
8* – speed sensor;
9* – a control lamp of malfunction of a control system;
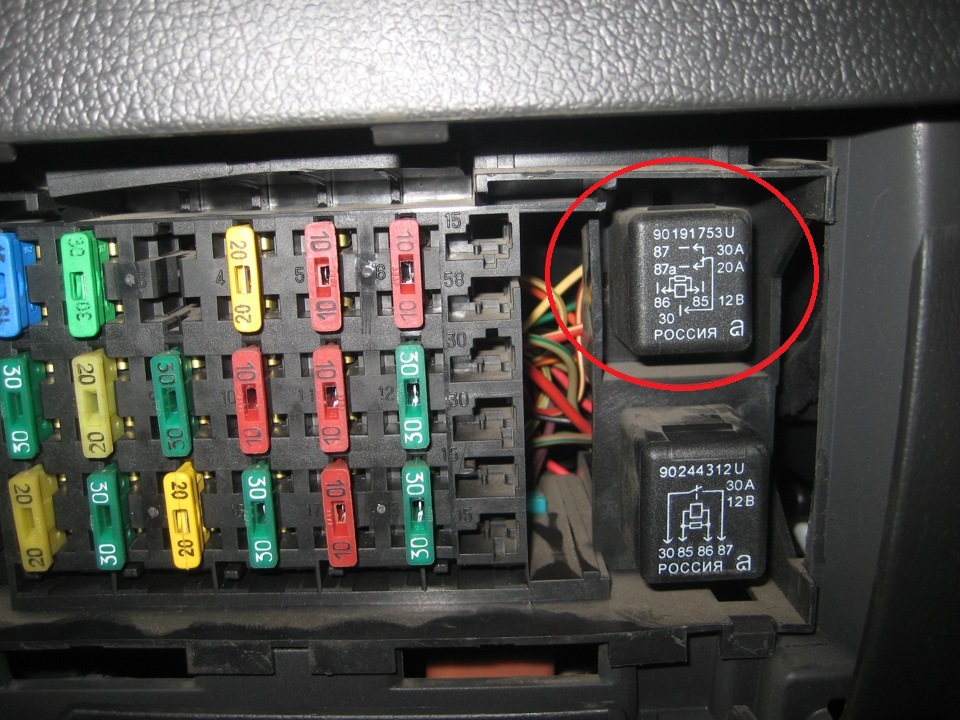
10* - mounting block of fuses and relays;
11 - battery;
12 - electronic control unit;
13* – wheel speed sensor;
14 - ignition coils;
15* - crankshaft position sensor;
16* – control oxygen concentration sensor;
17* - spark plugs;
18* - diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor.
Note:
* - the element is not visible in the photo.
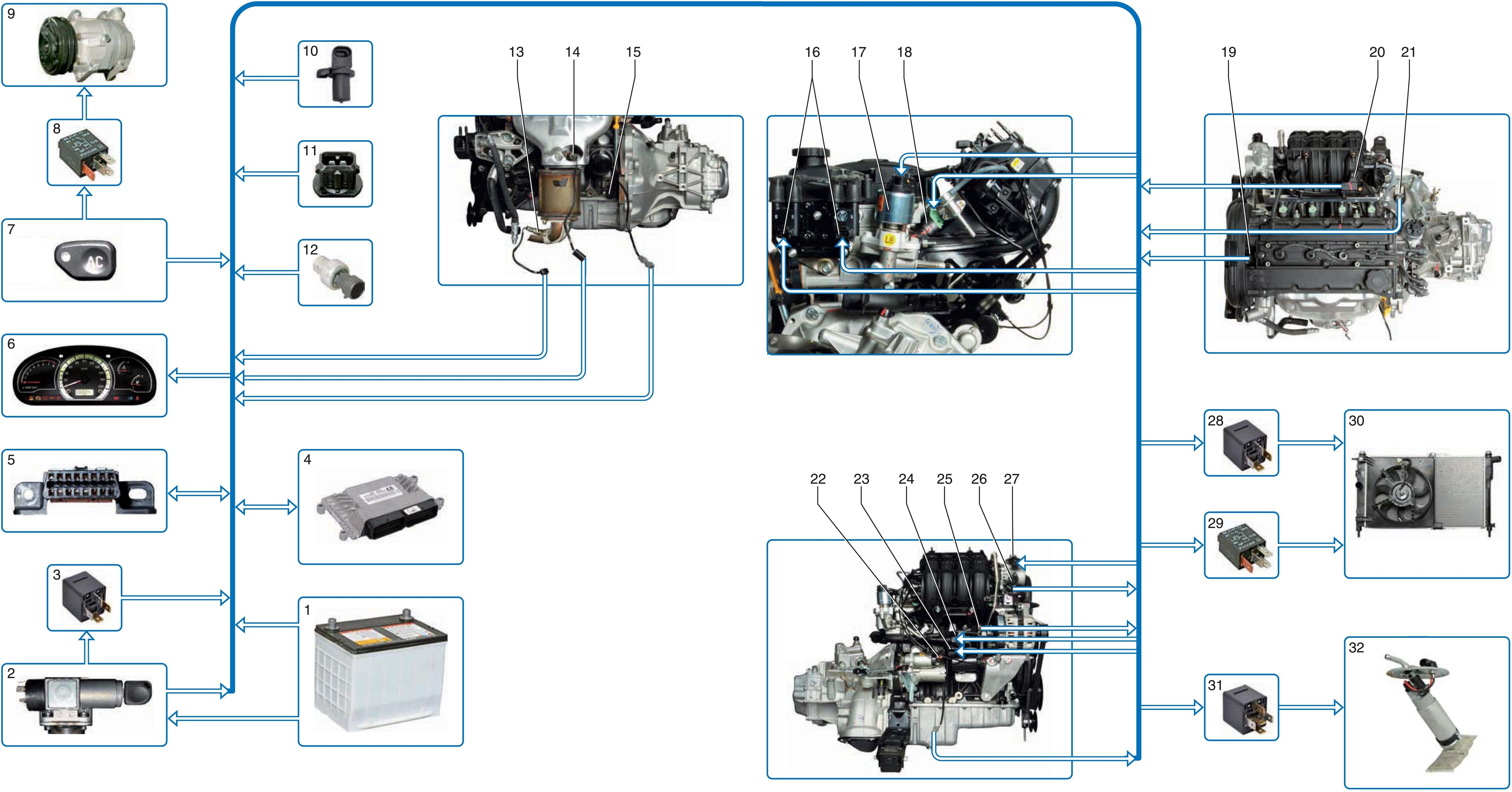
Scheme of the electronic engine control system F16D3 :
1 - rechargeable battery;
2 - ignition switch;
3 - ignition relay;
4 - ECU;
5 - diagnostic block;
6 – a combination of devices;
7 - air conditioner switch;
8 - air conditioner compressor relay;
9 - air conditioner compressor;
10 - wheel speed sensor;
11 - intake air temperature sensor;
12 - air conditioner refrigerant pressure sensor;
13 - diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor;
14 - control oxygen concentration sensor;
15 - crankshaft position sensor;
16 - ignition coils;
17 - exhaust gas recirculation valve;
18 - nozzle;
19 - phase sensor;
20 - sensor of absolute air pressure at the inlet;
21 - vehicle speed sensor;
22 - knock sensor;
23 - valve of the system for changing the length of the intake tract;
24 – adsorber purge valve;
25 - coolant temperature sensor;
26 - throttle position sensor;
27 - idle speed regulator;
28 - high speed relay of the fan of the cooling system;
29 - low speed relay of the fan of the cooling system;
30 - fan of the cooling system;
31 - fuel pump relay;
32 - fuel pump assembly.
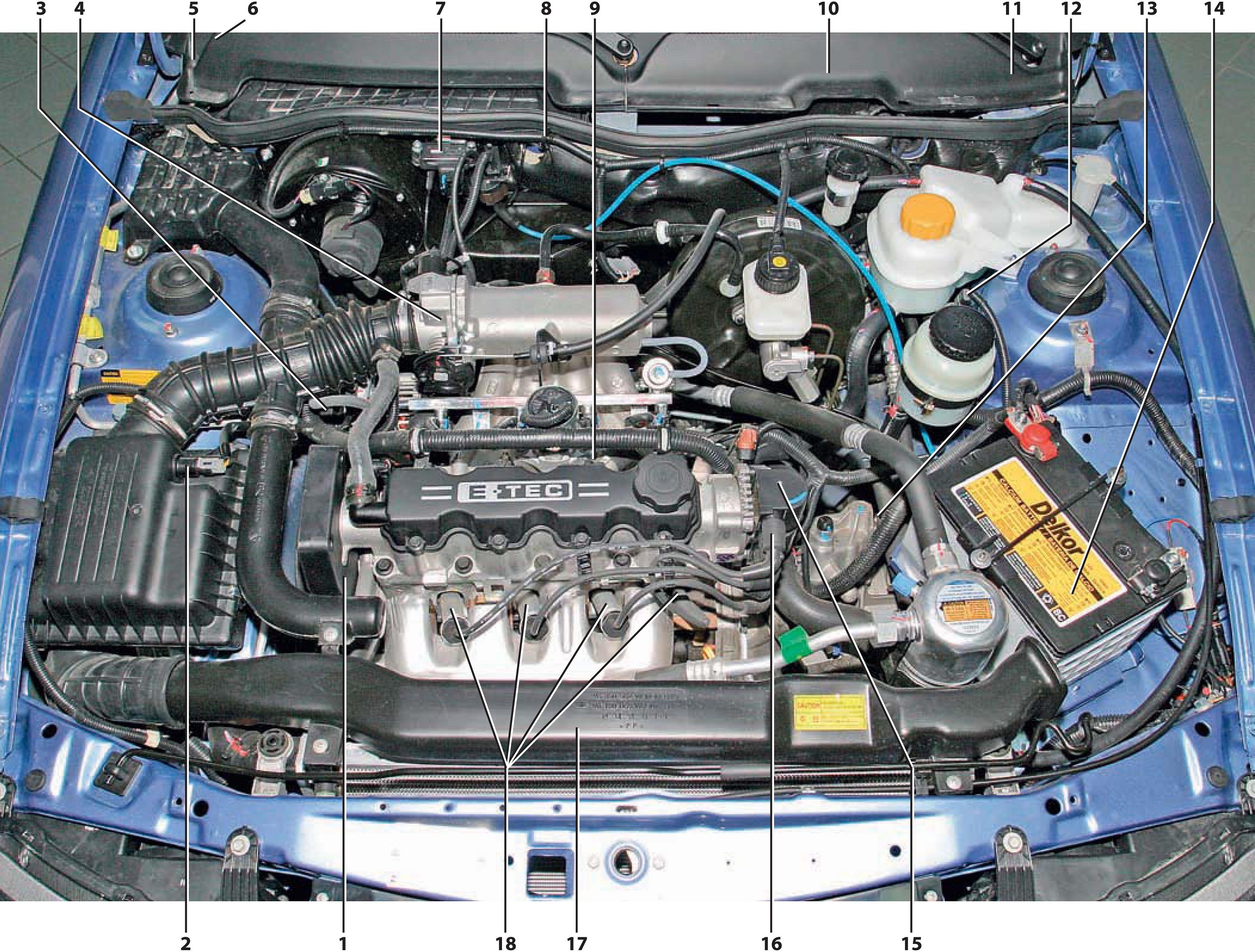
Elements of the electronic engine management system A15SMS :
1* - crankshaft position sensor;
2 - air temperature sensor at the inlet to the engine;
3 – phase sensor;
4* - throttle position sensor;
5* - diagnostic block;
6* – electronic control unit;
7 – the sensor of absolute pressure of air on an inlet;
8* – diagnostic oxygen concentration sensor;
9* - knock sensor;
10* - a control lamp of malfunction of a control system;
11* - mounting block of fuses and relays;
12 – rough road sensor;
13* – speed sensor;
14 - battery;
15 - ignition coil;
16* - coolant temperature sensor;
17* – control oxygen concentration sensor;
18* - spark plugs.
Note:
* - the element is not visible in the photo.
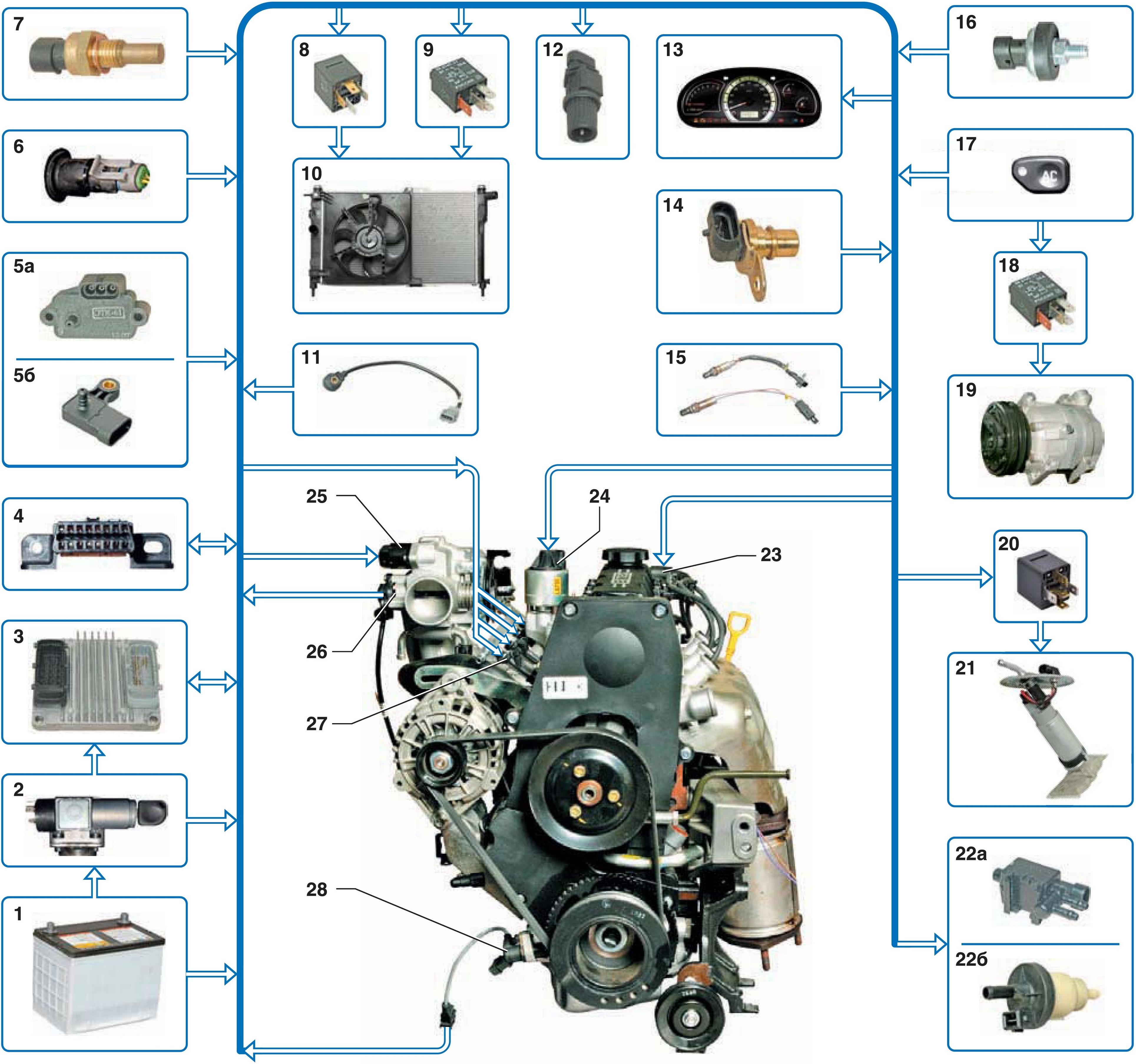
Diagram of the electronic engine management system A15SMS :
1 - rechargeable battery;
2 - ignition switch;
3 - ECU;
4 - block diagnostics;
5a, 5b – intake air absolute pressure sensor;
6 - intake air temperature sensor;
7 - coolant temperature sensor;
8 - high speed relay of the fan of the cooling system;
9 - low speed relay of the fan of the cooling system;
10 - fan of the cooling system;
11 - knock sensor;
12 - vehicle speed sensor;
13 – a combination of devices;
14 - phase sensor;
15 - control and diagnostic oxygen concentration sensors;
16 - rough road sensor;
17 - air conditioner switch;
18 - air conditioner compressor relay;
19 - air conditioning compressor;
20 - fuel pump relay;
21 - fuel pump assembly;
22a, 22b - adsorber purge valve;
23 - ignition coil;
24 - exhaust gas recirculation valve;
25 - idle speed regulator;
26 - throttle position sensor;
27 - nozzles;
28 - crankshaft position sensor.
ECU (controller)is a special purpose minicomputer. It consists of random access memory (RAM) and programmable read only memory (PROM). RAM is used by the microprocessor for temporary storage of current information about the operation of the engine (measured parameters) and calculated data. From the RAM, the engine control unit takes programs and raw data for processing. Fault codes are also stored in the RAM. This memory is volatile, i.e. when the power supply is interrupted (the battery is disconnected or the wiring harness block is disconnected from the computer), its contents are erased. PROM stores the engine control program, which contains a sequence of operating commands (algorithms) and calibration data - settings. PROM is non-volatile, i.e. The contents of the memory do not change when the power is turned off. The ECU receives information from the sensors of the system and controls the actuators, such as the fuel pump and injectors, the ignition coil, the idle speed controller, the heating element of the oxygen concentration sensor, the canister purge valve, the exhaust gas recirculation valve, the valve for the system for changing the length of the intake tract (on the F16D3 engine ), air conditioning compressor clutch, cooling fan.
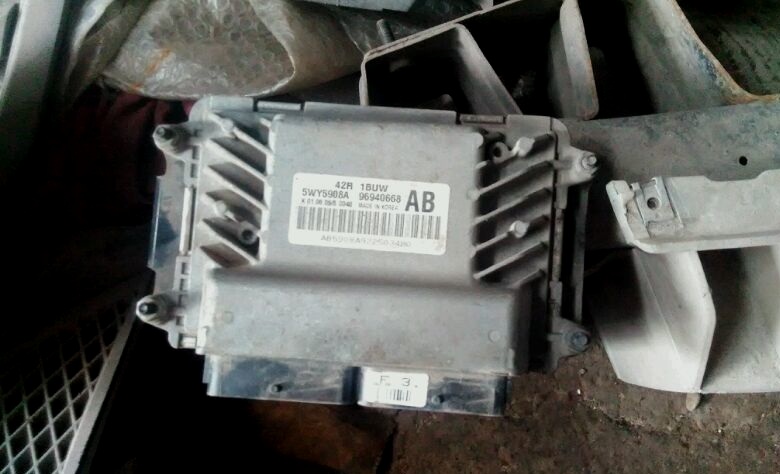

ECU (controller) of the F16D3 engine
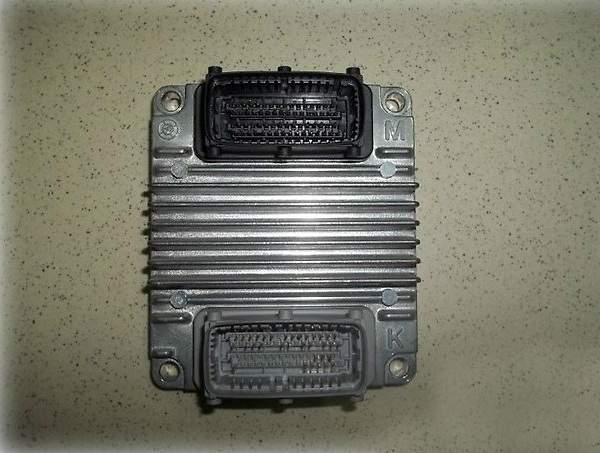

Engine ECU (controller) A15SMS
The electronic control unit on a car with an F16D3 engine is located in the engine compartment in front of the battery, and on a car with an A15SMS engine - in the car interior under the instrument panel on the right (under the side trim).
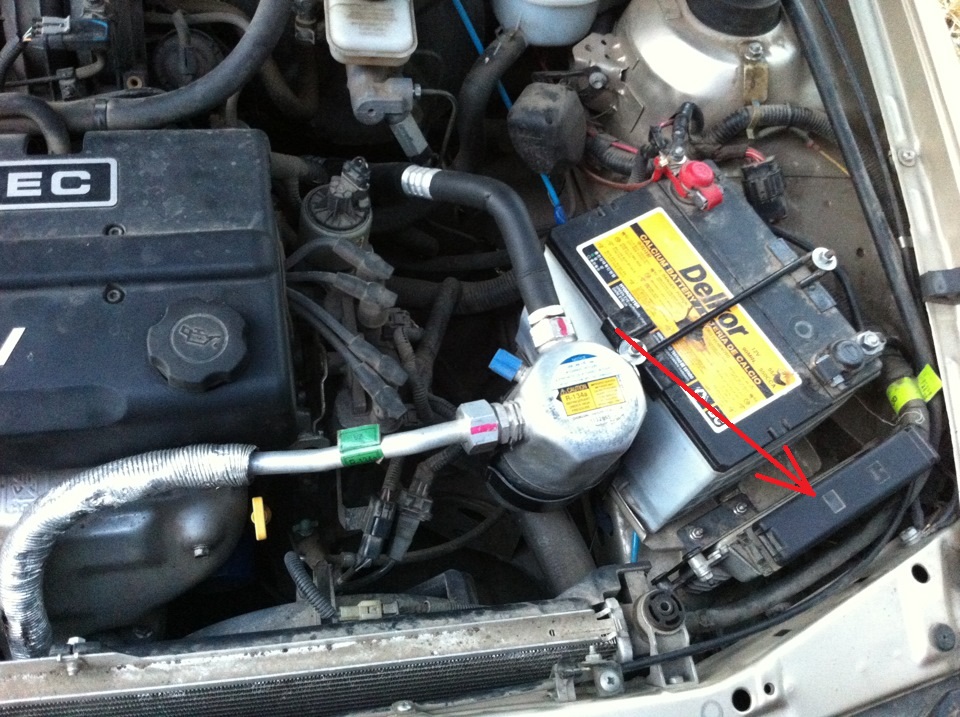

Placement of the ECU (controller) of the F16D3 engine
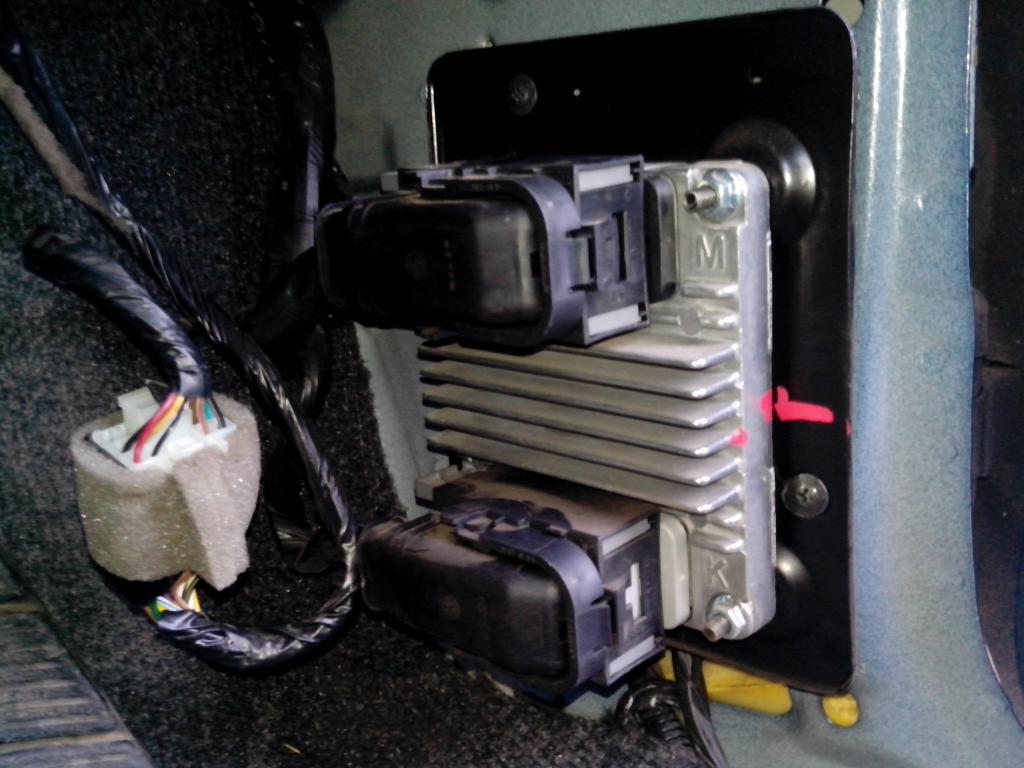

Placement of the ECU (controller) of the A15SMS engine
In addition to supplying voltage to the sensors and controlling actuators, the ECU performs diagnostic functions of the engine management system (on-board diagnostic system): it detects the presence of malfunctions of elements in the system, turns on the malfunction indicator lamp in the instrument cluster and stores fault codes in its memory. If a malfunction is detected, in order to avoid negative consequences (burning out of the pistons due to detonation, damage to the catalytic converter in the event of misfires in the air-fuel mixture, exceeding the limit values for exhaust gas toxicity, etc.), the ECU switches the system to emergency operating modes. Their essence is that in case of failure of any sensor or its circuit, the engine control unit uses replacement data stored in its memory.
The control lamp of malfunction of a control system of the engine is located in a combination of devices.
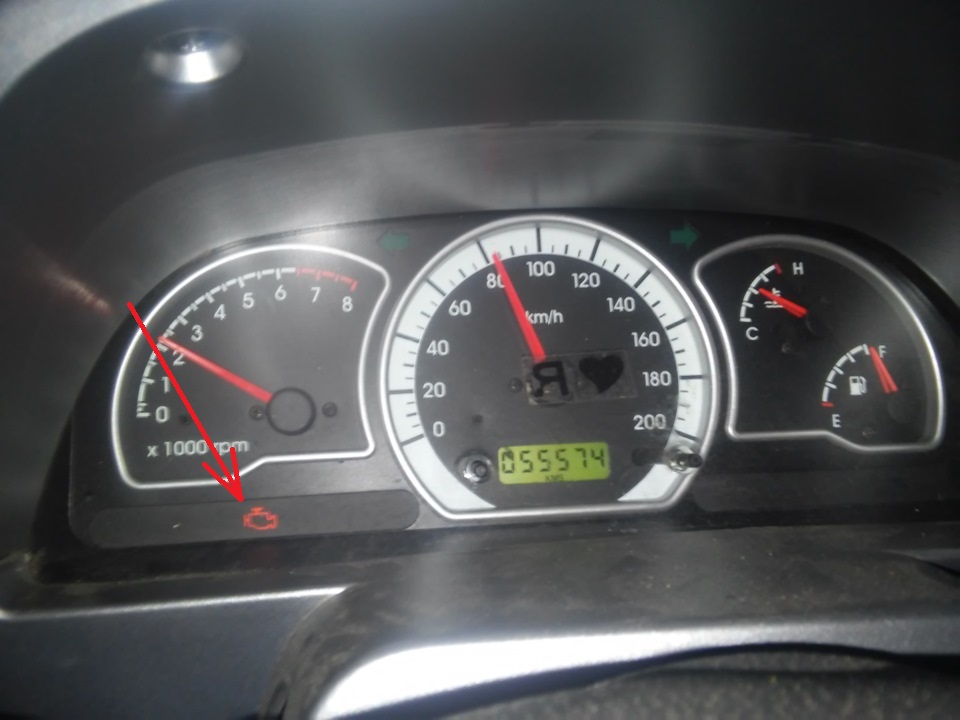

Placement of a control lamp of malfunction of a control system of the engine in a combination of devices
If the system is working, then when the ignition is turned on, the control lamp should light up. Thus, the ECU checks the health of the lamp and control circuit. After starting the engine, the control lamp should go out if there are no conditions in the computer memory for it to turn on. Turning on the lamp when the engine is running informs the driver that the on-board diagnostic system has detected a malfunction, and further movement of the car occurs in emergency mode. In this case, some engine operation parameters (power, throttle response, economy) may deteriorate, but movement with such malfunctions is possible, and the car can drive to the service station on its own.
If the fault was temporary, the ECU will turn off the lamp for three trips without a fault.
Fault codes (even if the lamp is off) remain in the unit's memory and can be read using a special diagnostic tool - a scanner that is connected to the diagnostic block.
The diagnostic block (diagnostic connector) is located in the passenger compartment under the instrument panel on the right (under the side trim).

Location of the diagnostic connector
For access to block of diagnostics take out a cap of an upholstery of the right sidewall.
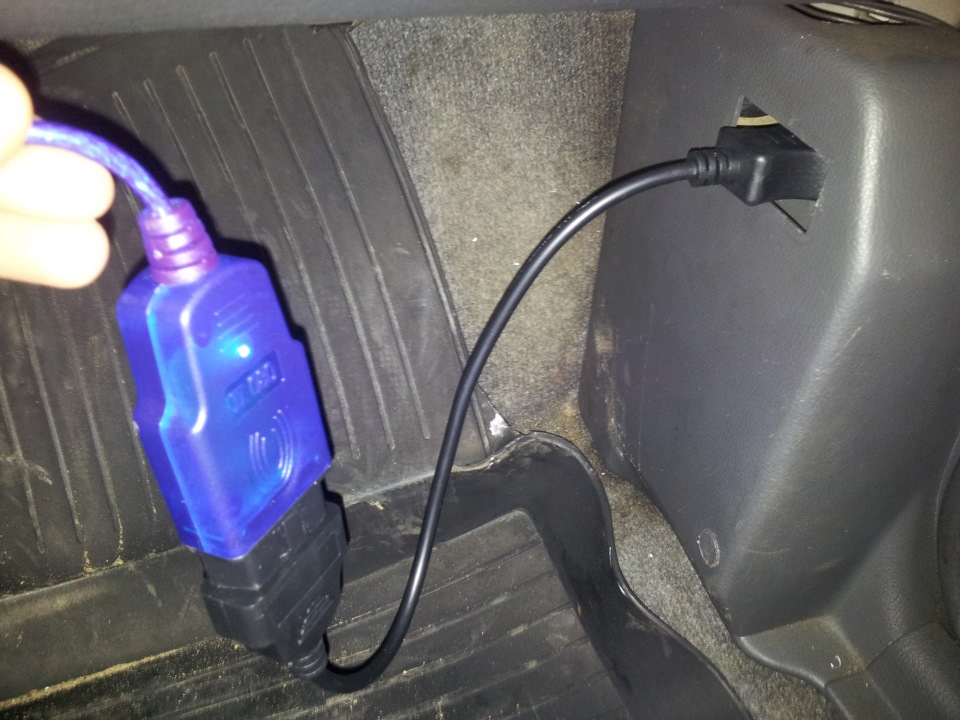

Access to the diagnostic socket
When the fault codes are cleared from the memory of the electronic unit using the diagnostic tool, the malfunction indicator lamp in the instrument cluster goes out.
The sensors of the control system give the ECU information about the parameters of the engine and the car, on the basis of which it calculates the moment, duration and order of opening of the fuel injectors, the moment and order of sparking.
The crankshaft position sensor on the F16D3 engine is located on the front wall of the cylinder block under the oil filter, and on the A15SMS engine it is located on the oil pump housing.
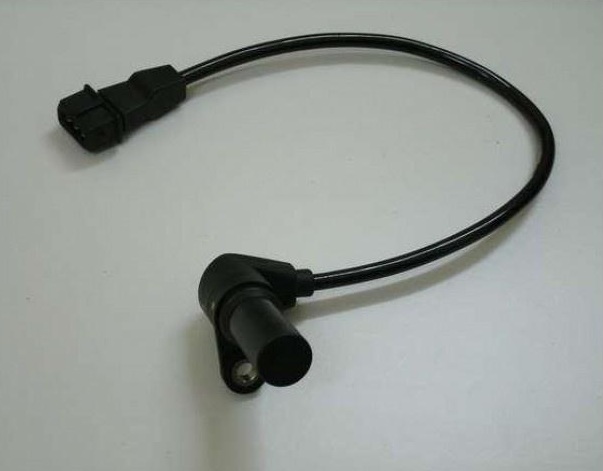

Engine crankshaft position sensor F16D3
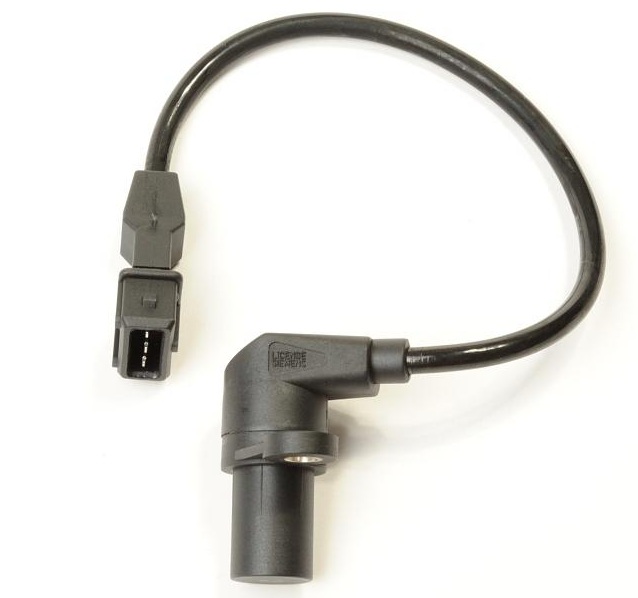

A15SMS engine crankshaft position sensor
The sensor gives the control unit information about the speed and angular position of the crankshaft. The sensor is of an inductive type, it reacts to the passage of the teeth of the setting disk near its core, attached to the cheek of the crankshaft of the 4th cylinder - on the F16D3 engine or combined with the auxiliary drive pulley - on the A15SMS engine. The teeth are located on the disk with an interval of 6 °. To determine the position of the crankshaft, two teeth out of 60 are cut off, forming a wide groove. When this groove passes by the sensor, a so-called “reference” synchronization pulse is generated in it.
The installation clearance between the sensor core and the tooth tips is approximately 1.3 mm. When the drive disk rotates, the magnetic flux in the magnetic circuit of the sensor changes - alternating current voltage pulses are induced in its winding. Based on the number and frequency of these pulses, the ECU calculates the phase and duration of the pulses for controlling the injectors and ignition coils.
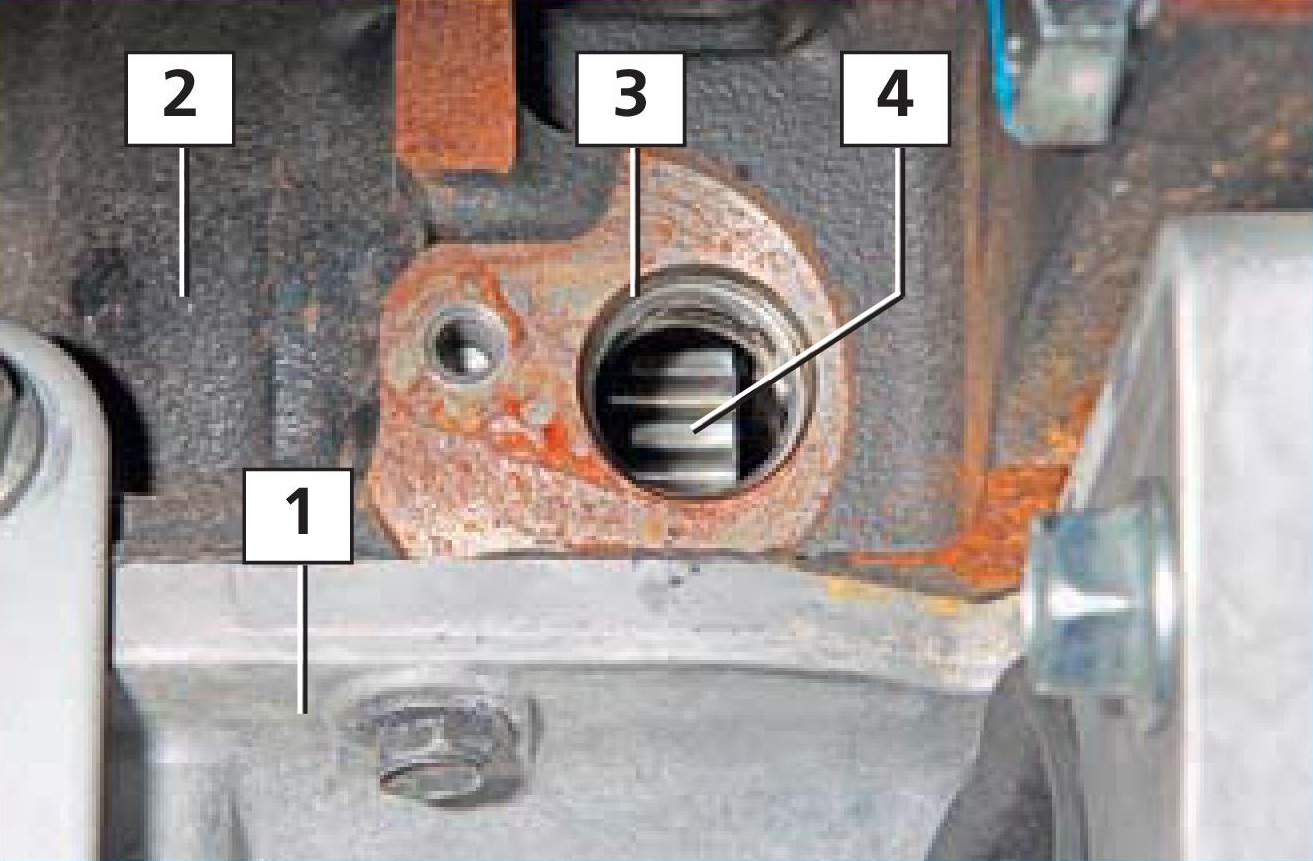
Installation location of the crankshaft position sensor on the F16D3 engine :
1 - oil pan;
2 - block of cylinders;
3 – sensor socket;
4 - the setting disk of the sensor.
The phase sensor (camshaft position) on the F16D3 engine is attached to the right end of the cylinder head next to the exhaust camshaft pulley. The phase sensor on the A15SMS engine is mounted on the rear wall of the camshaft bearing housing next to the camshaft sprocket.
The signal from the phase sensor is used by the ECU to coordinate the fuel injection processes in accordance with the order of operation of the cylinders. The principle of operation of the sensor is based on the Hall effect. To determine the position of the piston of the first cylinder during the working stroke on the F16D3 engine, the phase sensor responds to the passage of a protrusion made at the end of the exhaust camshaft pulley.
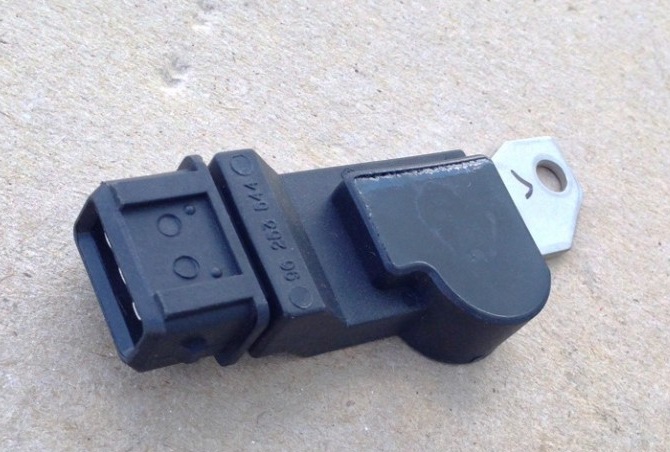

Engine phase sensor F16D3
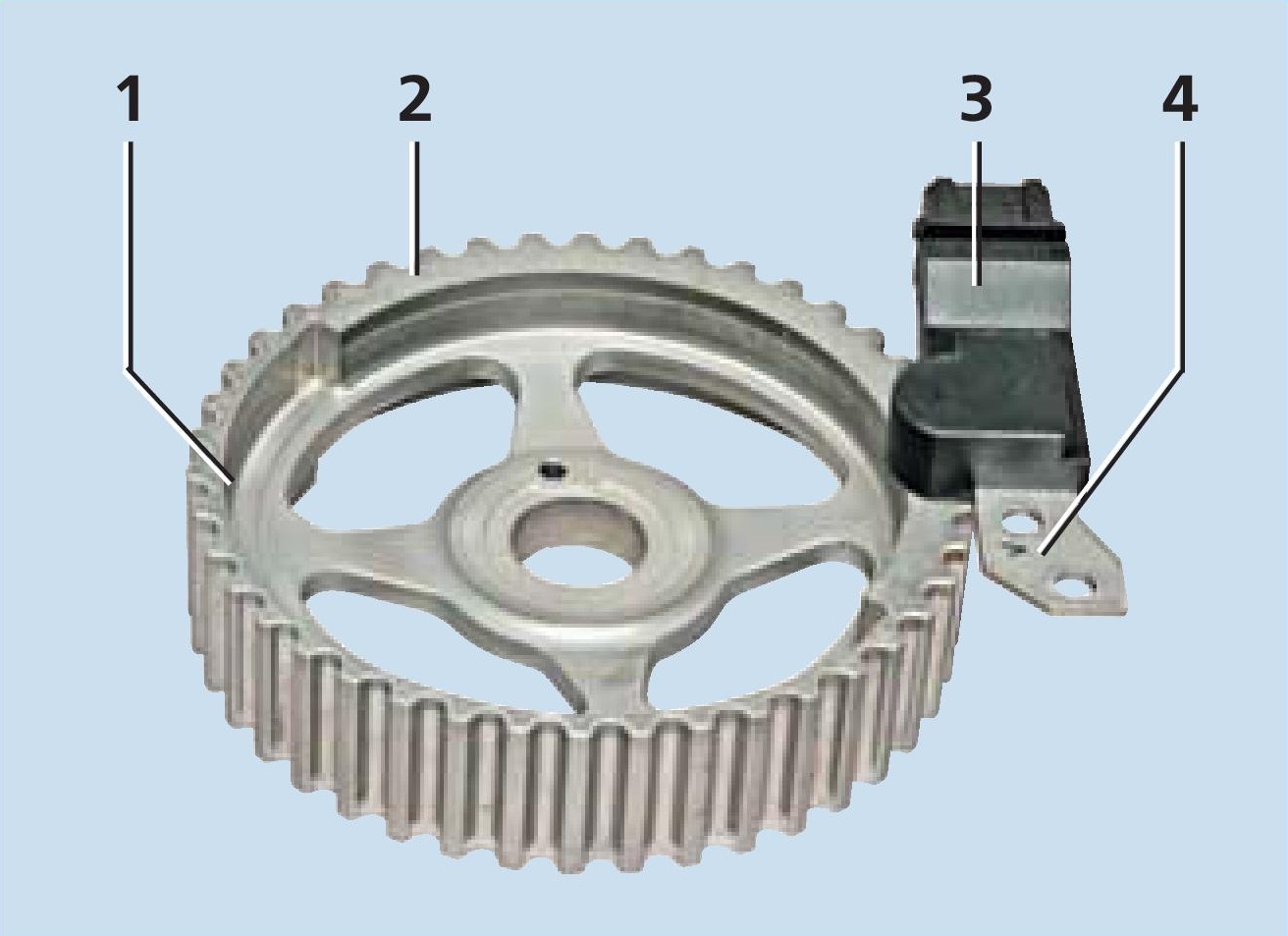
The mutual position of the phase sensor and the exhaust camshaft pulley on the F16D3 engine (for clarity, shown on the dismantled parts):
1 - camshaft pulley;
2 - ledge;
3 – sensor;
4 – sensor mounting plate.
On the A15SMS engine, the sensor reacts to the passage of a tide made on the toe of the camshaft.
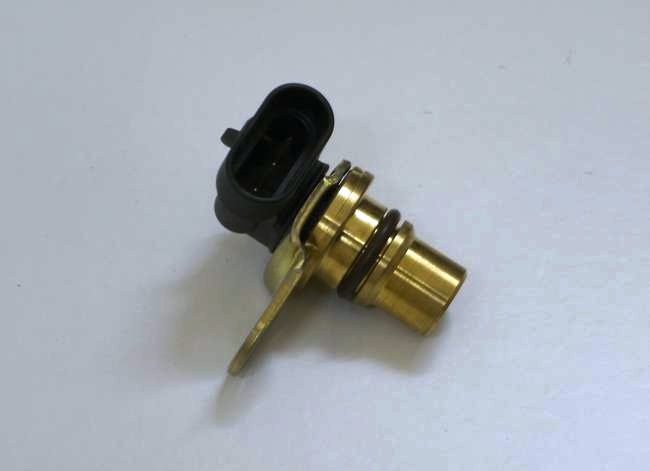

Motor phase sensor A15SMS
Depending on the angular position of the shaft, the sensor outputs rectangular voltage pulses of different levels to the control unit. Based on the output signals of the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors, the control unit sets the ignition timing and determines the cylinder into which fuel should be supplied. If the phase sensor fails, the ECU switches to the non-phased fuel injection mode.
The coolant temperature sensor on the F16D3 engine is screwed into the threaded hole in the rear wall of the cylinder head, between the air supply channels of the 1st and 2nd cylinders. On the A15SMS engine, the sensor is installed on the left side of the cylinder head. The sensor rod is washed by the coolant circulating through the cooling jacket of the cylinder head.
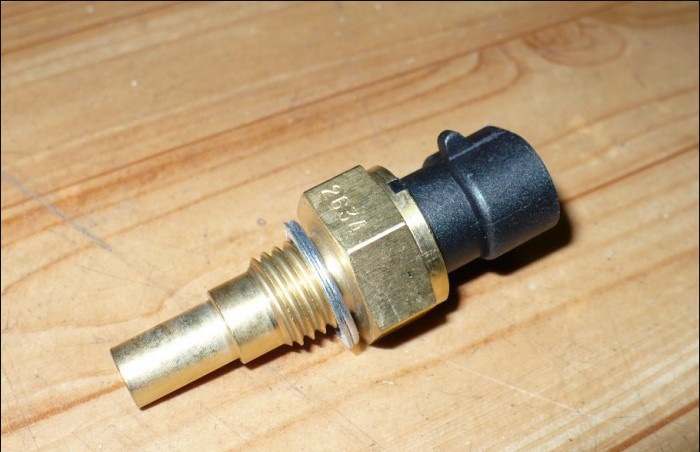

Coolant temperature sensor for F16D3 and A15SMS engines
The sensor is an NTC thermistor, i.e. its resistance decreases with increasing temperature. The ECU supplies a stabilized voltage of +5.0 V to the sensor through a resistor and, based on the voltage drop across the sensor, calculates the coolant temperature, the values of which are used to adjust the fuel supply and ignition timing.
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the throttle shaft and is a potentiometric type resistor.
A stabilized voltage of +5.0 V is supplied to one end of its resistive element from the ECU, and the other end is connected to the "mass" of the electronic unit. From the third output of the potentiometer (slider), which is connected to the throttle valve axis, a signal is taken for the control unit. By periodically measuring the output voltage of the sensor signal, the ECU determines the current throttle position to calculate the ignition timing and the duration of the fuel injection pulses, as well as to control the idle speed controller.
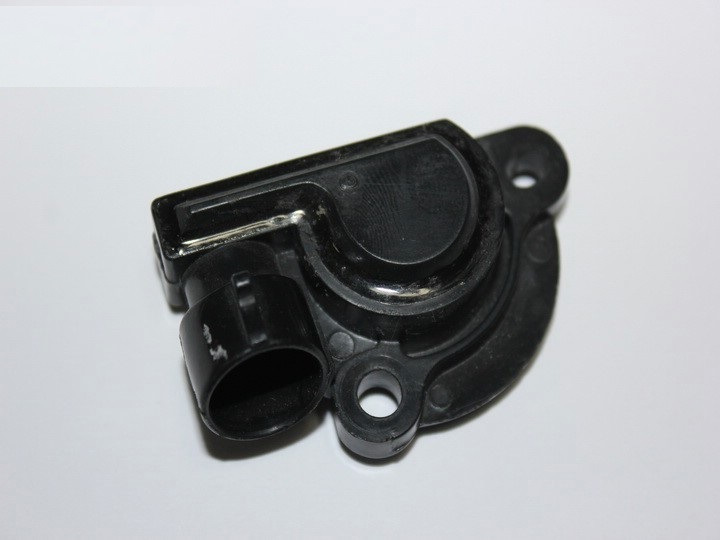

Throttle position sensor for F16D3 and A15SMS engines
Absolute pressure (vacuum) air intake sensor evaluates changes in air pressure in the intake manifold receiver, which depend on the load on the engine and the speed of its crankshaft, and converts them into voltage output signals. Based on these signals, the ECU determines the amount of air entering the engine and calculates the required amount of fuel. To supply more fuel at a large throttle opening angle (the vacuum in the intake manifold is negligible), the ECU increases the operating time of the fuel injectors. With a decrease in the throttle opening angle, the vacuum in the intake manifold increases and the ECU, processing the signal, reduces the operating time of the injectors.
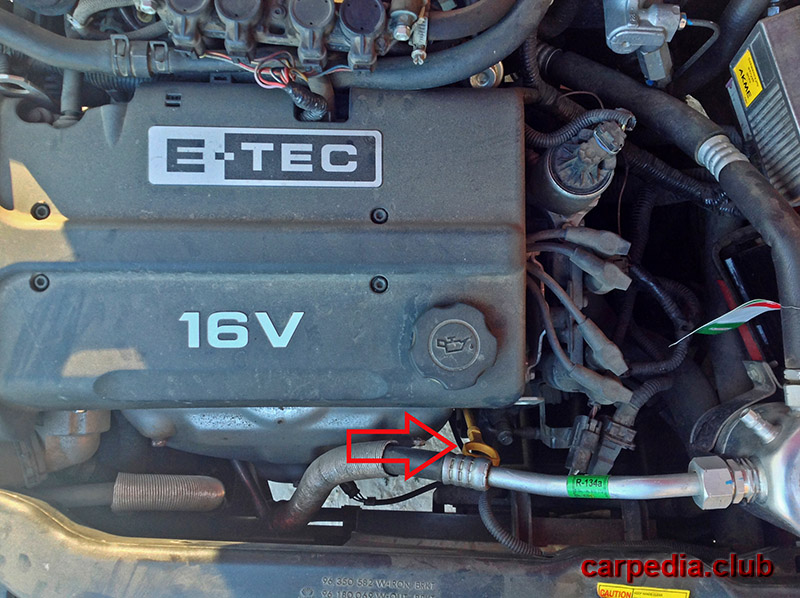
On a car with an F16D3 engine, the absolute air pressure sensor is attached to the intake manifold housing and connected by a tube to its receiver.
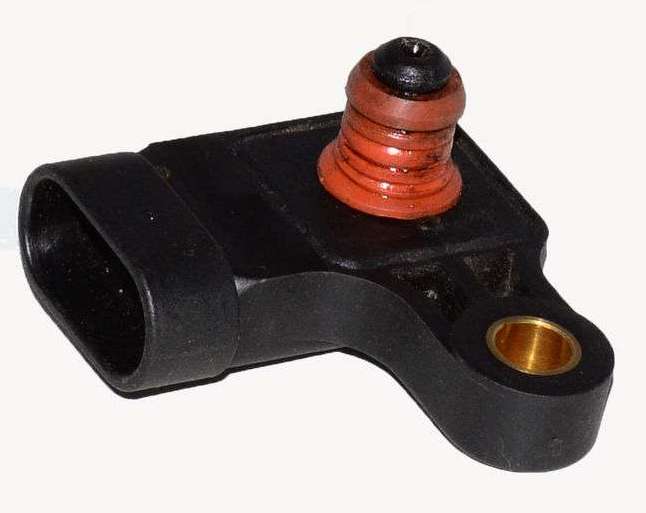

Intake absolute pressure sensor used on F16D3 and A15SMS engines
On a car with an A15SMS engine, two versions of absolute air pressure sensors are used, which are attached to the bulkhead and connected to the intake manifold receiver by a tube. In the first option, the sensor is exactly the same as on a car with an F16D3 engine (see photo above). In the second option, the sensor is different.
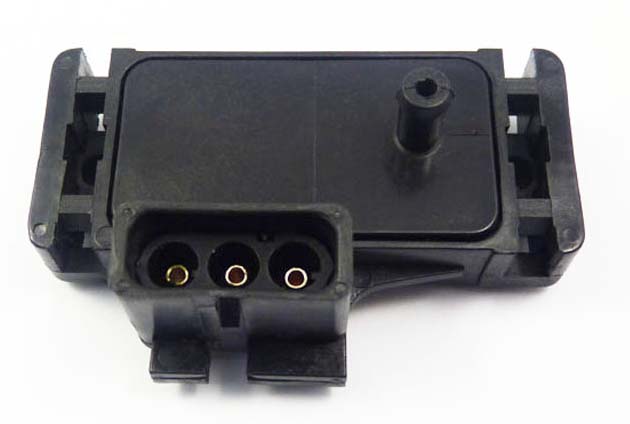

Intake absolute pressure sensor used on a vehicle with an A15SMS engine
The intake air temperature sensor on a car with an F16D3 engine is mounted in a corrugated air supply hose to the throttle assembly. On a vehicle with an A15SMS engine, the sensor is mounted in the air filter cover. The sensor is a thermistor (with the same electrical characteristics as the coolant temperature sensor) that changes its resistance depending on the air temperature. The ECU applies a stabilized voltage of +5.0 V to the sensor through a resistor and measures the change in signal level to determine the intake air temperature. The signal level is high when the air in the pipeline is cold and low when the air is hot. The information received from the sensor is taken into account by the ECU when calculating the air flow to correct the fuel supply and the ignition timing.
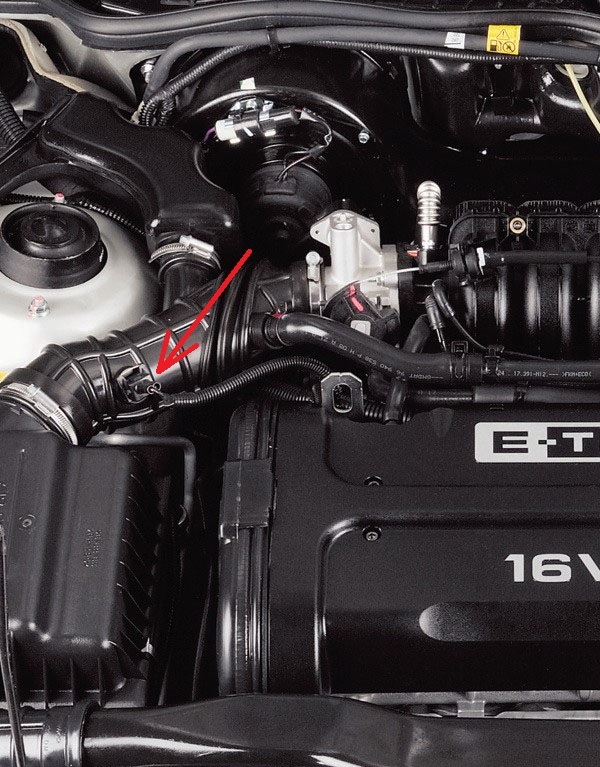
Location of engine air temperature sensor F16D3

A15SMS Engine Air Temperature Sensor Location
The knock sensor on both engines is mounted on the rear wall of the cylinder block in the area of the 3rd cylinder.

Knock sensor for F16D3 and A15SMS engines
The piezoceramic sensitive element of the knock sensor generates an alternating voltage signal, the amplitude and frequency of which correspond to the vibration parameters of the engine block wall. When detonation occurs, the amplitude of vibrations of a certain frequency increases. At the same time, to suppress knocking, the ECU corrects the ignition timing in the direction of later ignition.
In the control system of both engines, two oxygen concentration sensors are used - control and diagnostic.
The control oxygen concentration sensor on both engines is installed in the exhaust manifold.
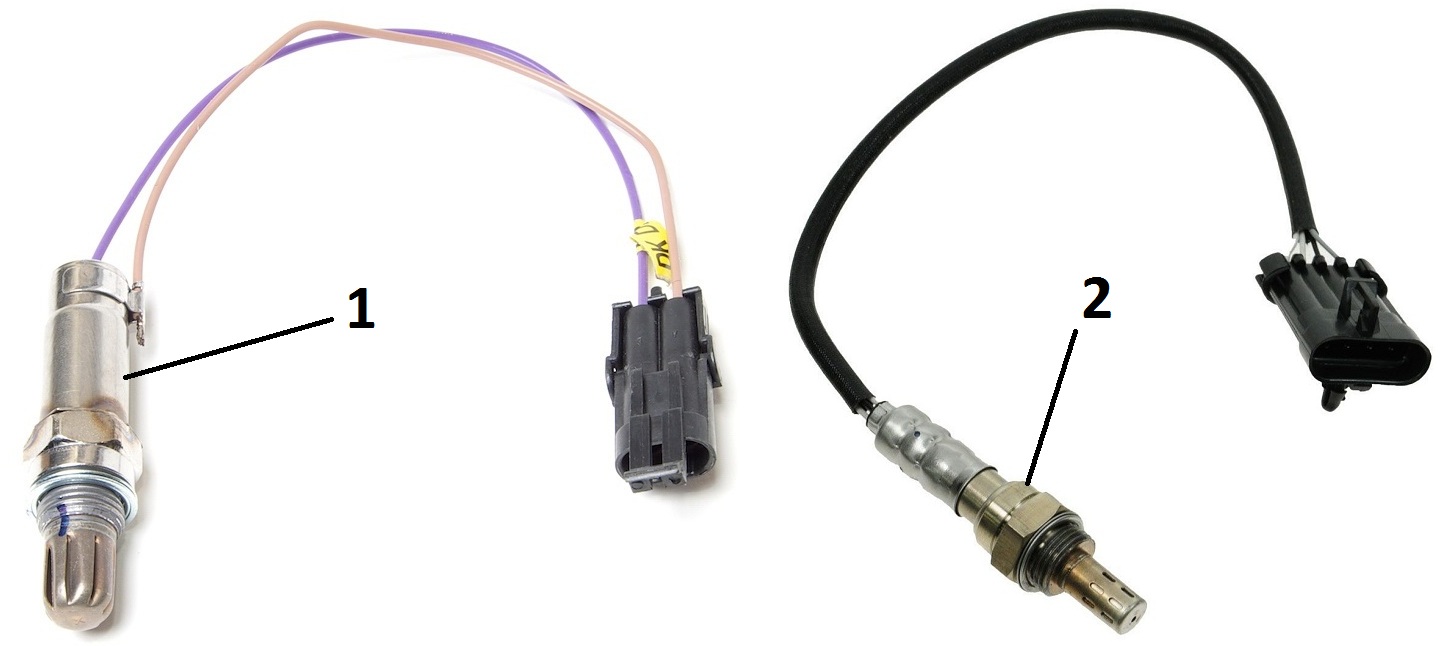
Oxygen concentration sensors for F16D3 and A15SMS engines :
1 - manager;
2 - diagnostic.
The sensor is a galvanic current source, the output voltage of which depends on the oxygen concentration in the environment surrounding the sensor. Based on the signal from the sensor about the presence of oxygen in the exhaust gases, the ECU adjusts the fuel supply by the injectors so that the composition of the working mixture is optimal for the efficient operation of the exhaust gas catalytic converter. The oxygen contained in the exhaust gases, after entering into a chemical reaction with the sensor electrodes, creates a potential difference at the sensor output, varying from approximately 0.1 to 0.9 V.
A low signal level corresponds to a lean mixture (the presence of oxygen), and a high signal level corresponds to a rich one (no oxygen). When the sensor is cold, there is no output from the sensor because its internal resistance in this state is very high - a few MΩ (the engine control system operates in an open loop). For normal operation, the temperature of the oxygen concentration sensor must be at least 300°C. In order to quickly warm up the sensor after starting the engine, a heating element is built into the sensor, which is controlled by the ECU. As the sensor warms up, the resistance drops and it begins to generate an output signal. Then the ECU starts to take into account the signal from the oxygen concentration sensor for fuel control in closed loop mode.
The oxygen sensor can be "poisoned" by the use of leaded gasoline or by the use of sealants containing large amounts of highly volatile silicone (silicon compounds) when assembling the engine. Silicone vapors can enter through the crankcase ventilation system into the combustion chamber of the engine. The presence of lead or silicon compounds in the exhaust gases can lead to sensor failure. In the event of a failure of the sensor or its circuits, the ECU controls the fuel supply in an open loop.
The diagnostic oxygen sensor on a vehicle with an F16D3 engine is installed after the catalytic converter in the intermediate pipe of the exhaust system. On a vehicle with an A15SMS engine, the sensor is installed in the pipe of the additional muffler after the additional catalytic converter. The main function of the sensor is to evaluate the efficiency of the exhaust gas catalytic converter. The signal generated by the sensor indicates the presence of oxygen in the exhaust gases after the catalytic converter. If the catalytic converter is operating normally, the diagnostic sensor reading will differ significantly from the control sensor reading. The principle of operation of the diagnostic sensor is the same as that of the control oxygen concentration sensor.
The vehicle speed sensor is mounted on the transmission clutch housing from above, next to the gearshift mechanism.
Vehicle speed sensor
The principle of operation of the speed sensor is based on the Hall effect. The sensor drive gear is engaged with the gear mounted on the differential box. The sensor outputs rectangular voltage pulses to the computer with a frequency proportional to the speed of rotation of the drive wheels. The number of sensor pulses is proportional to the distance traveled by the vehicle. The ECU determines the speed of the car by the frequency of the pulses.
The F16D3 engine management system uses a wheel speed sensor that provides information to the electronic control unit.

Wheel speed sensor
The sensor is attached to the steering knuckle of the left front wheel. The sensor is of an inductive type, it reacts to the passage of the teeth of the driving disk near its core, which is made on the body of the outer hinge of the left wheel drive.
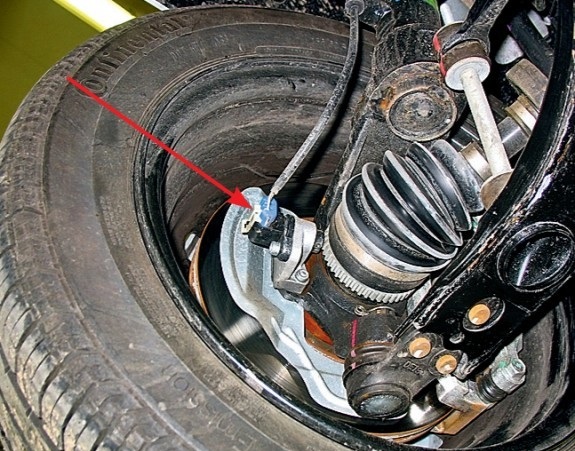

Location of the wheel speed sensor on a car with an F16D3 engine
The A15SMS engine management system uses a rough road sensor installed in the engine compartment on the left mudguard cup.
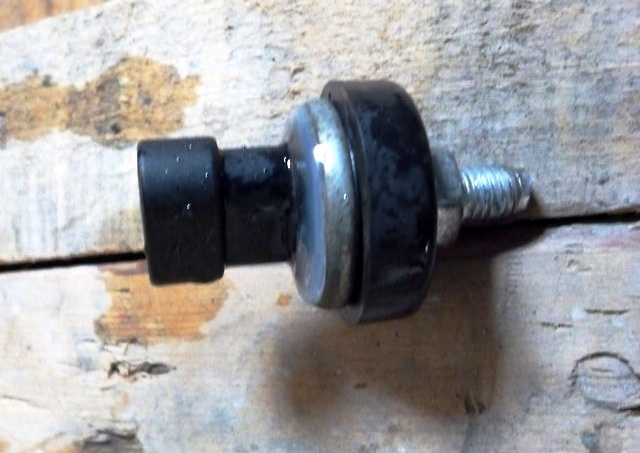

Rough road sensor
The rough road sensor is designed to measure the amplitude of body vibrations. The variable load on the transmission that occurs when driving on rough roads affects the angular speed of rotation of the engine crankshaft. At the same time, oscillations in the frequency of rotation of the crankshaft are similar to similar oscillations that occur during misfires of the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders. In this case, to prevent false detection of misfiring in cylinders, the ECU disables this function of the on-board diagnostic system when the sensor signal exceeds a certain threshold.
The ignition system is part of the engine management system and consists of an ignition coil (on the F16D3 engine - 2 pcs.), high-voltage wires and spark plugs. In operation, the system does not require maintenance and adjustment, except for the replacement of candles. The control of the current in the primary windings of the coils is carried out by the ECU, depending on the operating mode of the engine. Spark plug wires are connected to the terminals of the secondary (high-voltage) windings of the coils: to one coil of the 1st and 4th cylinders, to the other - of the 2nd and 3rd. Thus, the spark simultaneously jumps in two cylinders (1-4 or 2-3) - in one at the end of the compression stroke (working spark), in the other at the end of the exhaust stroke (idle). The ignition coil is non-separable, in case of failure it is replaced.
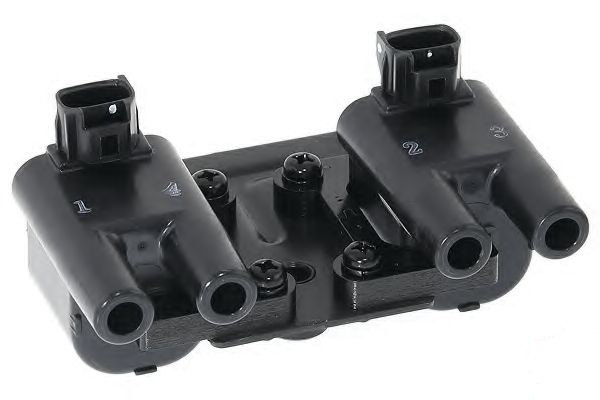

F16D3 engine ignition coil
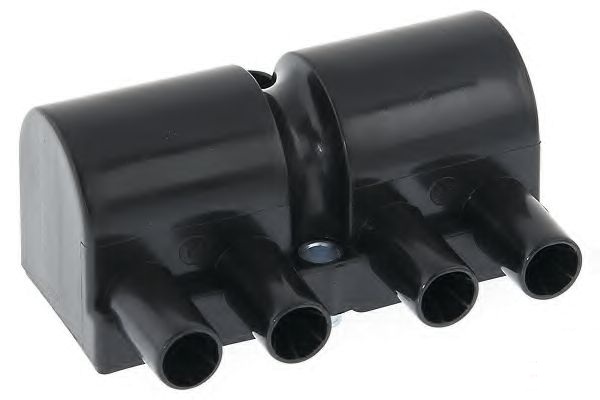

A15SMS engine ignition coil
The F16D3 engine uses NGK BKR6E-11 spark plugs or equivalents from other manufacturers. The gap between the electrodes of the candle is 1.0-1.1 mm. The size of the hexagon of the turnkey candle is 16 mm.
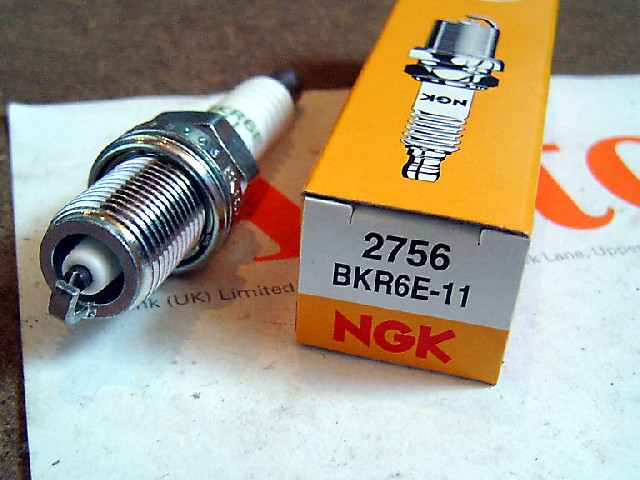

Engine spark plug F16D3
The A15SMS engine uses CHAMPION RN9YC, NGK BPR6ES spark plugs or equivalents from other manufacturers. The gap between the electrodes of the candle is 0.7-0.8 mm. The size of the turnkey hexagon is 21 mm.
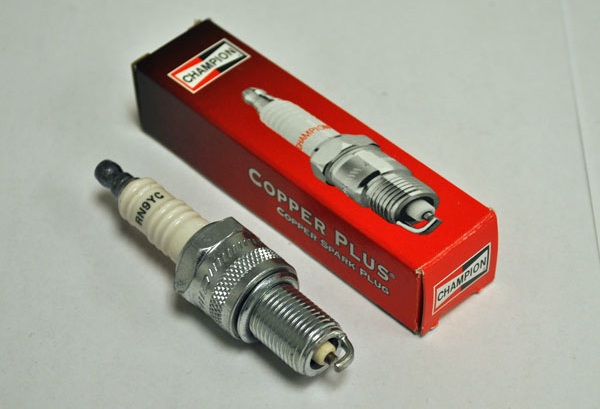

A15SMS engine spark plug
When the ignition is turned on, the ECU energizes the fuel pump relay for 2 seconds to create the necessary pressure in the fuel rail. If during this time cranking of the crankshaft by the starter has not begun, the ECU turns off the relay and turns it on again after the start of cranking.
If the engine has just been started and its speed is above 400 min -1, the control system operates in an open loop, not taking into account the signal from the control oxygen concentration sensor. At the same time, the ECU calculates the composition of the air-fuel mixture based on the input signals from the coolant temperature sensor and the engine intake air pressure sensor. After warming up the control oxygen concentration sensor, the system starts to work in a closed loop, taking into account the sensor signal. If, when trying to start the engine, it did not start and there is a suspicion that the cylinders are filled with excess fuel, they can be purged by fully depressing the “gas” pedal and turning on the starter. At this throttle position and crankshaft speed below 400 min-1, the ECU will turn off the injectors. When you release the "gas" pedal, when the throttle is less than 80% open, the ECU will turn on the injectors.
During engine braking (gear and clutch engaged), when the throttle is fully closed and the engine speed is high, fuel injection is not performed to reduce exhaust emissions.
When the voltage drops in the vehicle's on-board network, the ECU increases the energy accumulation time in the ignition coils (for reliable ignition of the combustible mixture) and the duration of the injection pulse (to compensate for the increase in nozzle opening time). With an increase in the voltage in the on-board network, the energy accumulation time in the ignition coils and the duration of the pulse supplied to the injectors decrease. When the ignition is turned off, the fuel supply is turned off, which prevents the mixture from spontaneous ignition in the engine cylinders.
Note:
When servicing and repairing the engine management system, always turn off the ignition (in some cases it is necessary to disconnect the wire terminal from the “negative” battery terminal). When carrying out welding work on a vehicle, disconnect the engine management system wiring harnesses from the ECU. Before drying the car in a drying chamber (after painting), remove the computer. With the engine running, do not disconnect or adjust the engine control harness connectors or the battery terminals. Do not start the engine if the wire terminals on the battery terminals and the lugs of the "mass" wires on the engine are loose or dirty.
Source: carpedia.club








![1 generation [2-й restyling] [2008 - 2016]](/uploads/Daewoo_Nexia_2008_-_2015_.jpg)
