Note:
Below is a description of the design of the Lada Grant front suspension to understand the placement and functionality of individual elements of the corresponding mechanisms.
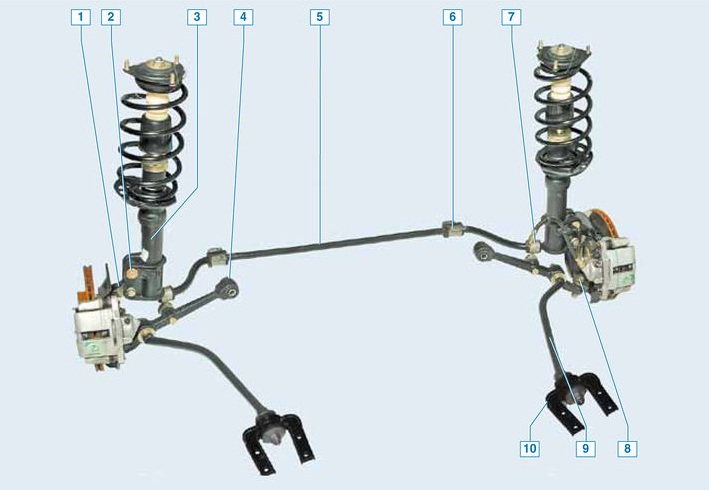
Front suspension:
1 – a rotary fist;
2 - eccentric bolt;
3 - shock absorber;
4 - lever;
5 – stabilizer bar;
6 - bracket for attaching the stabilizer bar cushion;
7 – stabilizer bar post;
8 - ball bearing;
9 - stretching;
10 - bracket.
The front suspension is independent with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers, helical barrel springs, wishbones, two stretch marks and an anti-roll bar.
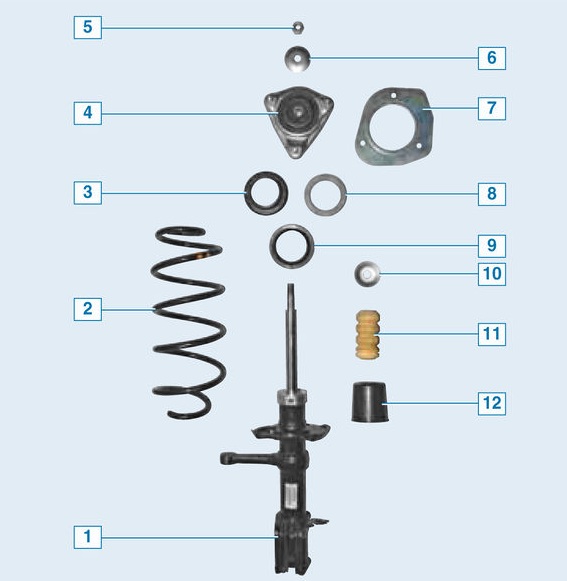
Suspension strut details:
1 - telescopic stand;
2 - spring;
3 - metal sleeve;
4 - upper support;
5 - rod nut;
6 - limiter of the rebound stroke of the upper support;
7 - base plate of the upper support;
8 - bearing;
9 - spring gasket;
10 - upper support compression stroke limiter;
11 – compression stroke buffer;
12 - protective cover.
The basis of the suspension is a telescopic hydraulic shock absorber strut, which serves as a guide and bearing device for the front suspension. The shock absorber strut allows the front wheels to move up and down when driving over bumps and at the same time dampen body vibrations.
A bracket for attaching the strut to the steering knuckle is welded to the lower part of the strut housing, and a spring support cup is welded to the middle part. The lower part of the rack is attached with two bolts and nuts to the steering knuckle.
The top bolt passing through the rack bracket hole has an eccentric collar and an eccentric washer. Turning this bolt adjusts the camber angle of the front wheel.
The telescopic strut is equipped with a helical barrel spring, a polyurethane foam buffer for the compression stroke, as well as an upper strut support assembly with a bearing. The outer coils of the barrel spring have a smaller diameter than the middle ones, which provides variable stiffness. When the spring is compressed, the less rigid coils (larger diameter) first approach, and then the more rigid ones.
Under the weight of the front of the car, the bearing is in a compressed position, which allows you to eliminate all gaps and knocks. When the wheels are turned, the strut body rotates along with the spring, but the shock absorber rod remains stationary and the shock absorber rod connection with the shock absorber guide sleeve wears out less.
A telescopic hydraulic shock absorber is installed in the rack housing.
The lower part of the steering knuckle is connected to the suspension arm through a ball joint. The support is attached to the steering knuckle with two screws (the holes in the steering knuckle are not through). When unscrewing these screws, be careful: they often break with considerable effort, so moisten them with penetrating liquid before disassembling. The ball joint pin is attached to the lever with a self-locking nut. The support is covered with a rubber-metal cover.

Elements of the front suspension on the car:
1 - bracket for attaching the stabilizer bar cushion;
2 – a pillow of a bar of the stabilizer;
3 – bars of the anti-roll bar;
4 - lever;
5 - stabilizer bar;
6 - shock absorber;
7 – rotary fist;
8 - ball bearing;
9 - stretching;
10 - extension bracket.
The suspension arms are connected to each other by an anti-roll bar through racks with rubber and rubber-metal hinges. The bar is made of spring steel.
The anti-roll bar is designed to increase lateral stability and reduce body roll angles by twisting the middle part of the bar when moving its ends.
Braking and traction forces during vehicle movement are perceived by longitudinal extensions connected through silent blocks to levers and brackets installed on the lower cross member of the radiator frame. Washers are installed at the connection points (at both ends of the brace) to adjust the angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the wheel.
The steering knuckle is equipped with a double-row closed-type angular contact ball bearing, which is fixed in the knuckle with two retaining rings. The wheel hub is installed in the inner rings of the bearing with an interference fit. The inner rings of the bearing are tightened (through the hub) with a nut on the shank of the outer hinge housing of the wheel drive. In operation, the bearing is not adjustable and does not require relubrication.
The wheel hub nuts are the same, with right-hand threads.
Note:
When replacing stretch marks, silent blocks, springs, upper supports of shock absorber struts, as well as when disconnecting the steering knuckle from the shock absorber strut, it is necessary to check and, if necessary, adjust the wheel alignment angles at the service station.
Source: http://wiki.zr.ru/173-2_Granta





![1 generation [2011 - 2017]](/uploads/Lada_Granta_2011_-_2015.jpg)
